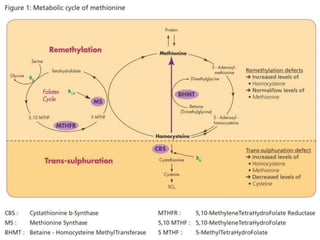
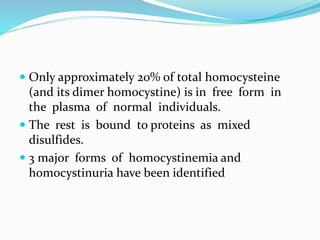
Homocystinuria is a disorder of methionine metabolism caused by an inability to metabolize homocysteine. There are three main types: classic homocystinuria caused by cystathionine β-synthase deficiency; defects in methylcobalamin formation; and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency. Symptoms vary but can include developmental delay, dislocated lenses, skeletal abnormalities, thromboembolism, and intellectual disability. Treatment depends on the type but may include vitamin B6, betaine, folic acid, vitamin B12, methionine supplementation, and dietary restrictions.