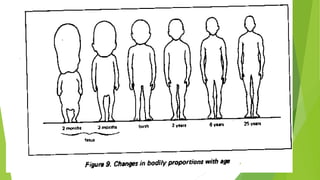
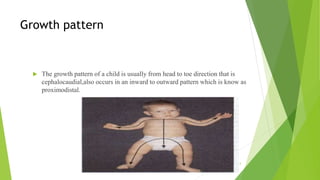
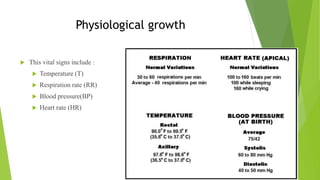
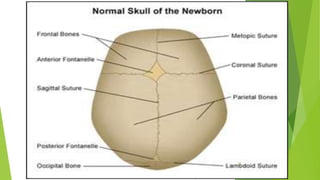
The document outlines the concepts of growth and development, highlighting definitions, importance, principles, factors influencing growth, types of growth, and stages of development. It details the physiological, physical, motor, cognitive, emotional, and social aspects of development across various age groups from prenatal to late childhood. Additionally, it emphasizes the unique patterns and milestones specific to each stage of a child's growth and development.