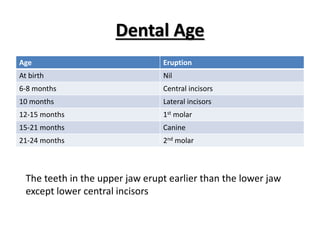
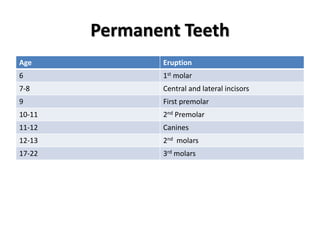
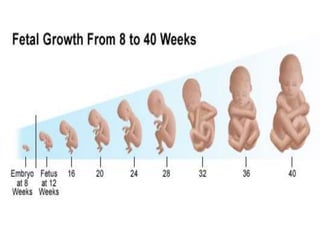
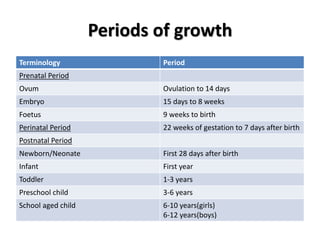
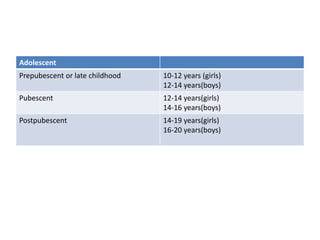
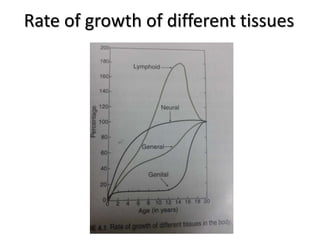
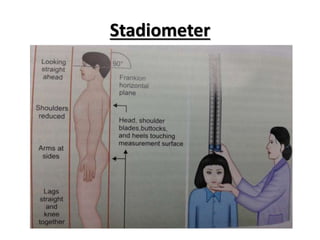
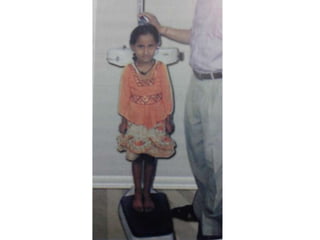
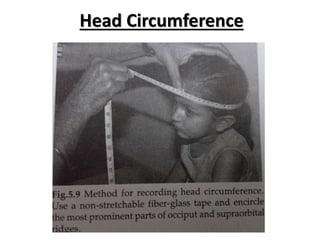
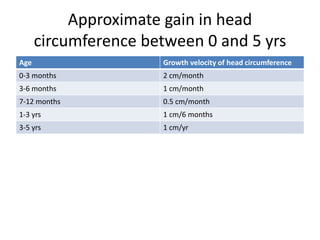
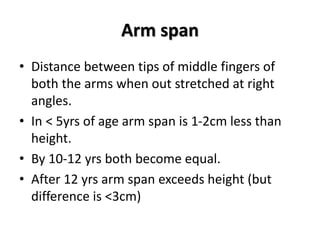
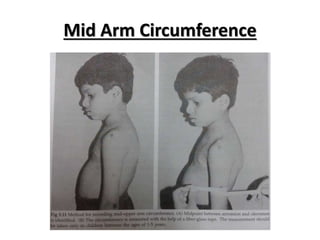
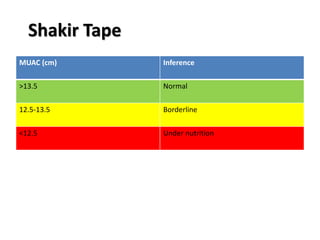
- Growth is the increase in size of organs and body, and is assessed through physical anthropometry such as weight, height, head circumference, and mid-upper arm circumference.
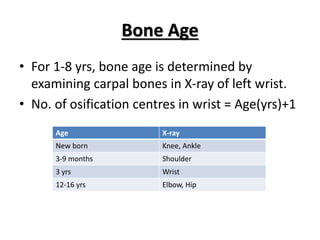
- Periodic growth assessment allows for early detection of growth faltering which can indicate undernutrition, infection, or disease.
- Factors like genetics, nutrition, hormones, environment, and socioeconomic status can influence growth.
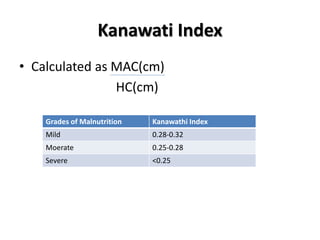
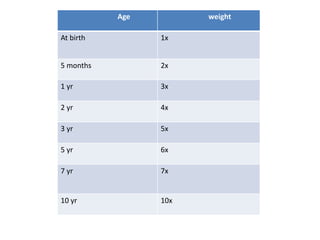
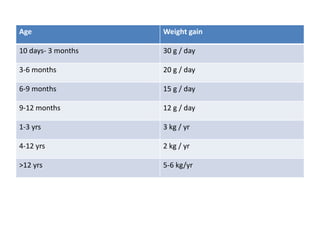
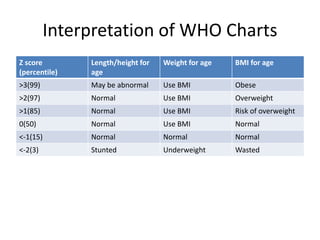
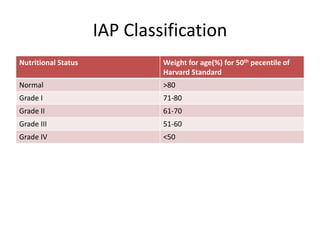
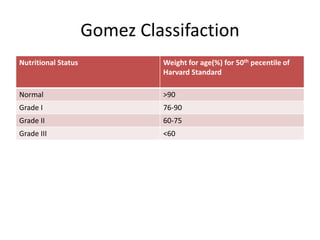
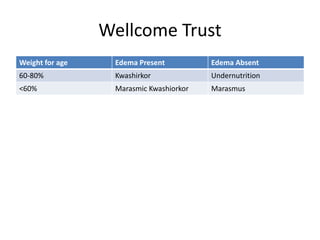
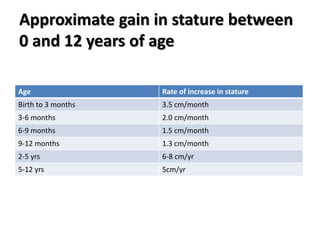
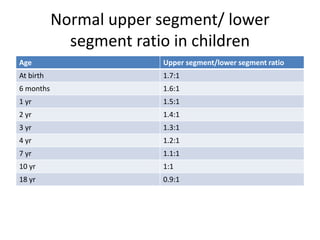
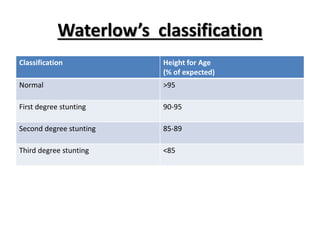
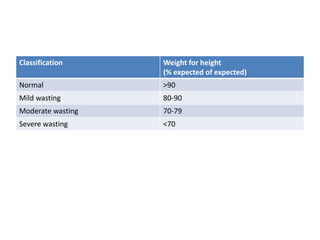
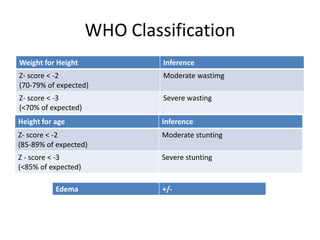
- Growth charts are used to evaluate if a child's growth is normal based on weight for age, height for age, and BMI for age.
- Deviations from normal growth patterns on charts may indicate malnutrition or underlying health conditions.





























![Body Mass Index
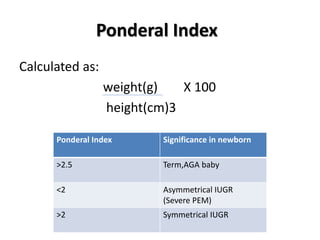
•Calculated as:
weight(kg) X 100
[Height(m)]2
•Nutritional intervention is required if BMI
<15 or less then 5th percentile in children.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/growth-151218080714/85/Growth-ASSESSMENT-58-320.jpg)