1. The document discusses growth and development from infancy through adolescence, outlining the key physical, cognitive, social, and emotional milestones at each stage.
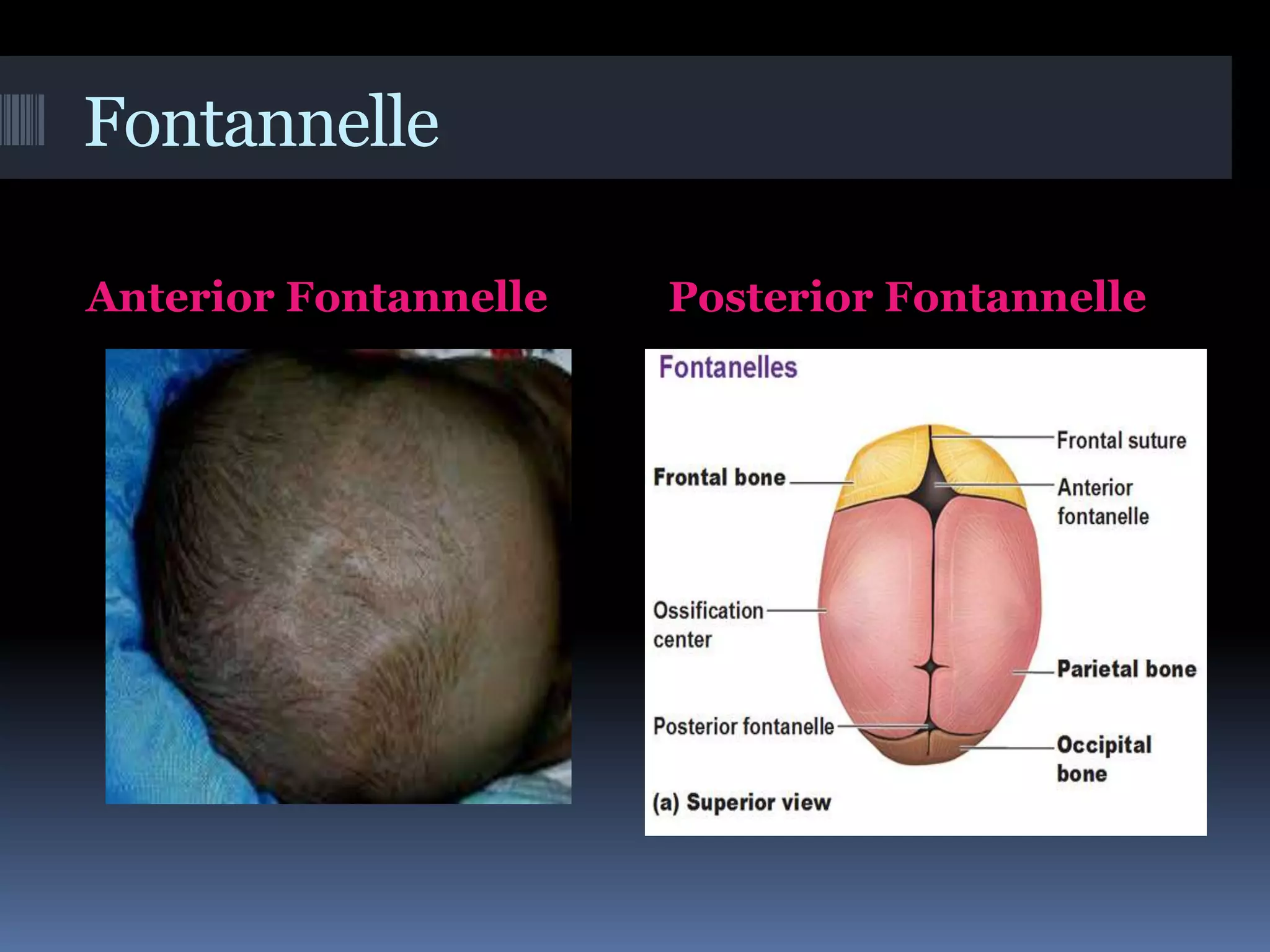
2. It provides details on growth patterns, assessing factors like weight, height, head circumference, and teething.
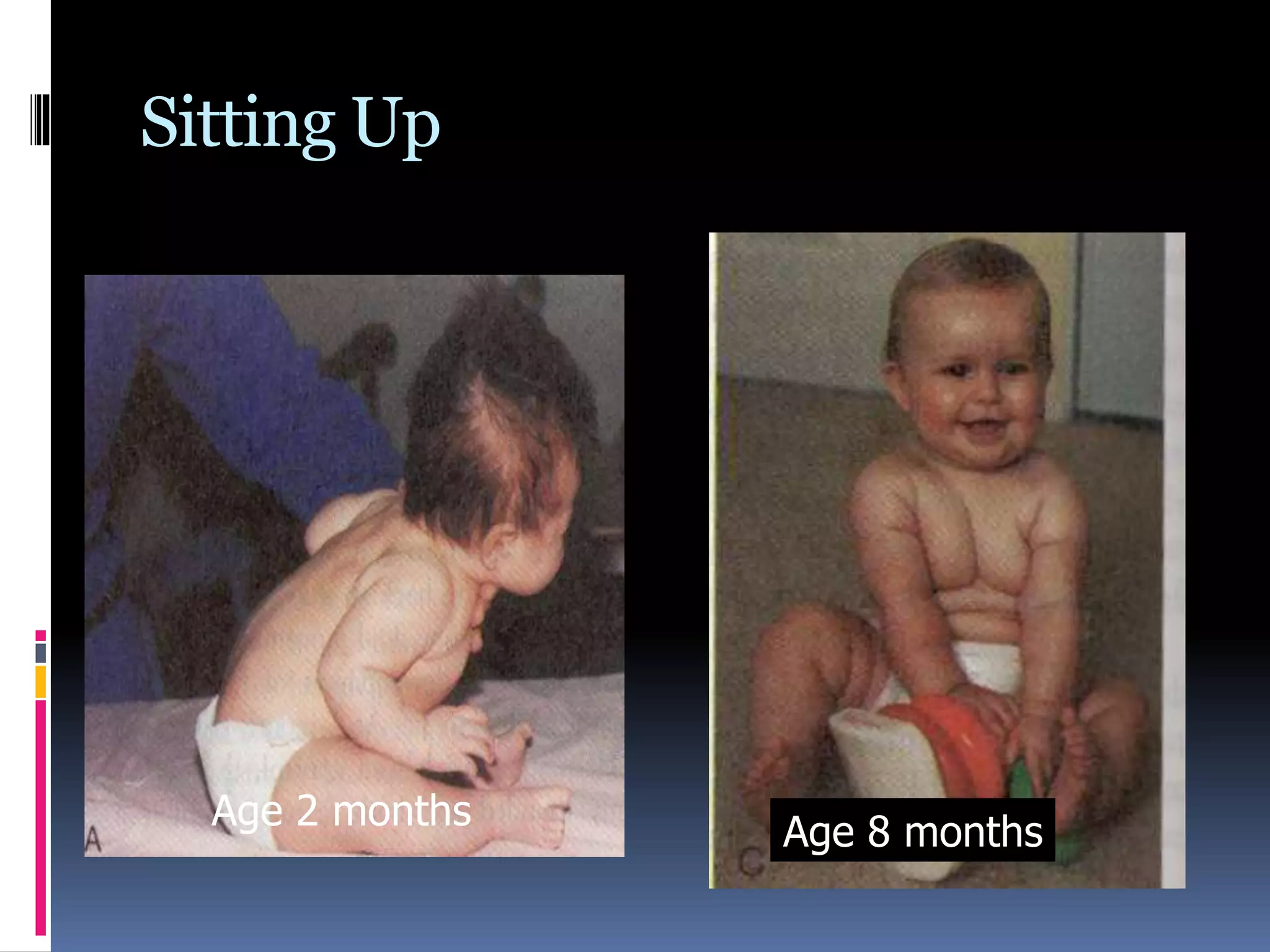
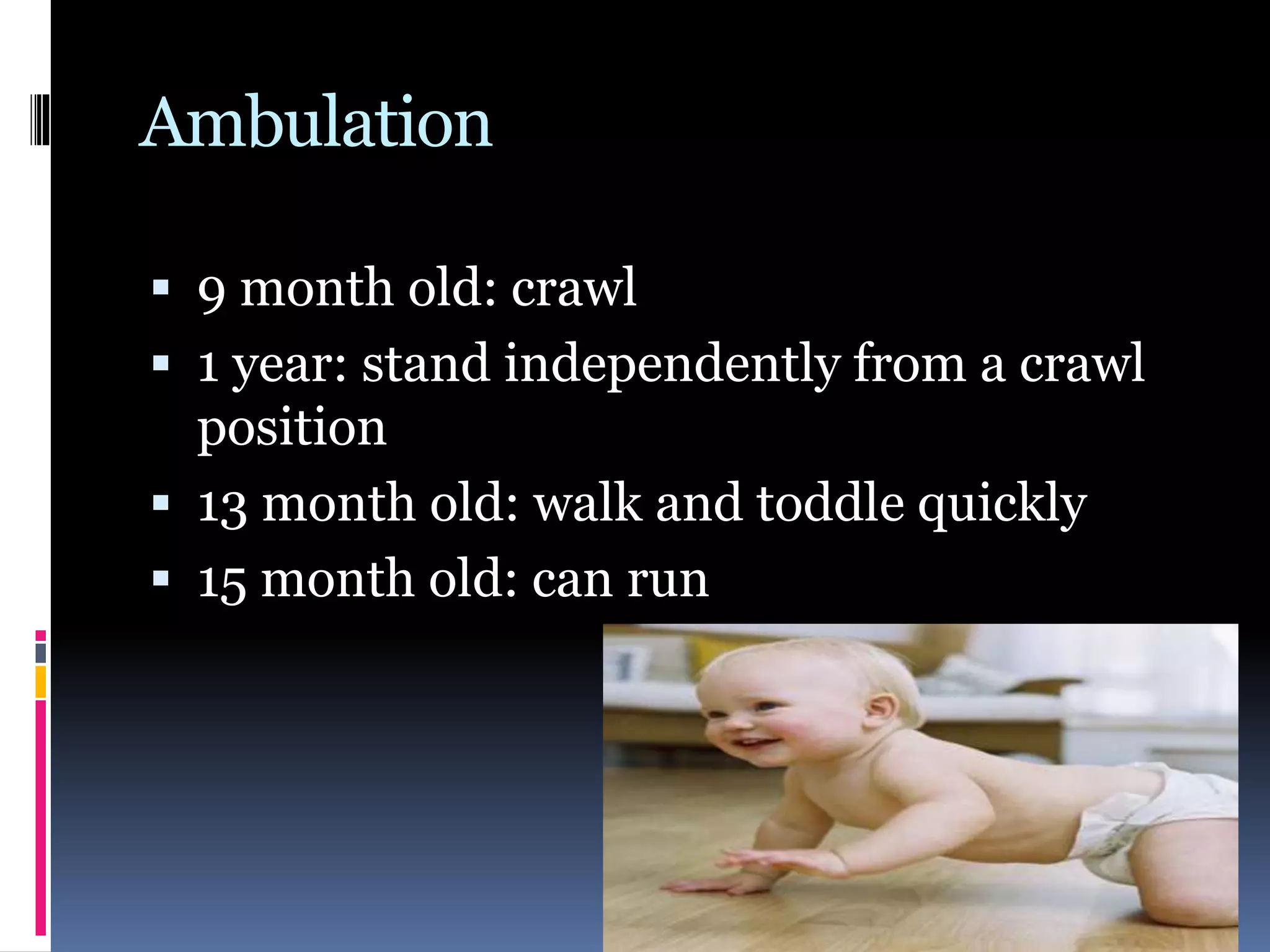
3. Developmental principles are outlined, noting growth proceeds from general to complex, in a head-to-toe direction, and is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors.