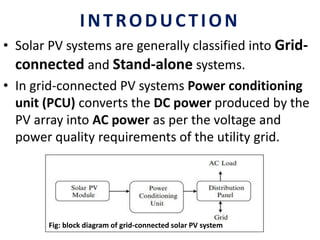
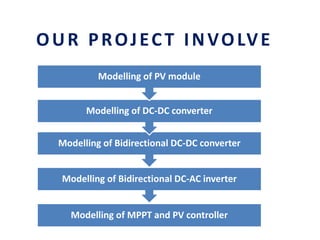
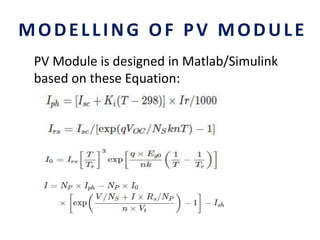
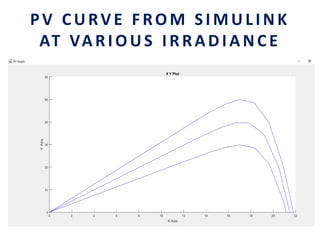
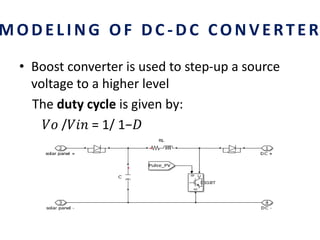
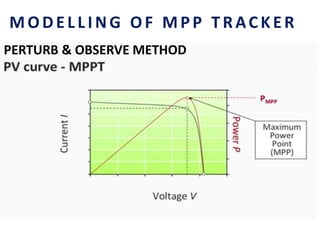
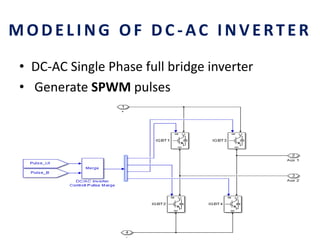
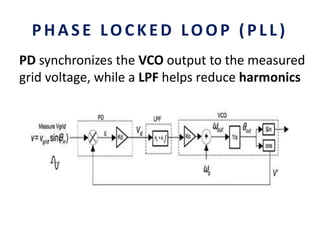
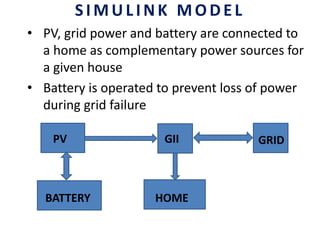
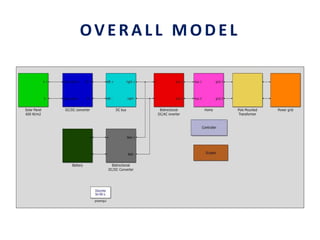
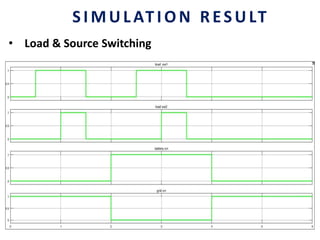
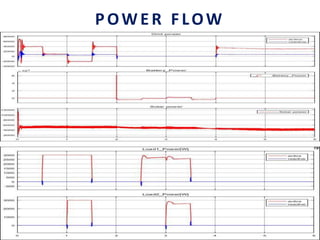
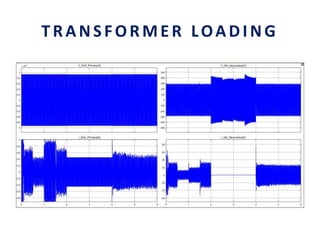
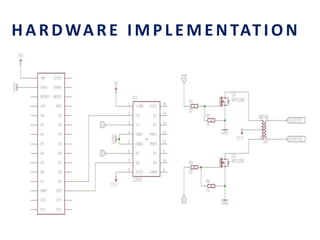
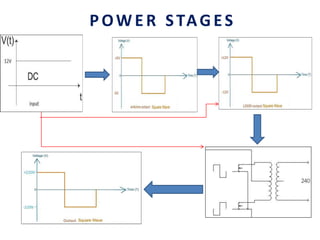
This document analyzes a grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) system. It discusses modeling different components of the system like the PV module, DC-DC converter, maximum power point tracker, DC-AC inverter, and phase locked loop for grid synchronization in MATLAB/Simulink. Simulation results show the power flow and transformer loading. The overall model demonstrates utilizing surplus PV power fed to the grid and deficient power from the grid to meet load demand. Future work could involve more advanced components and control strategies.