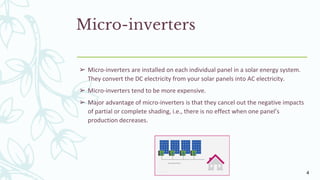
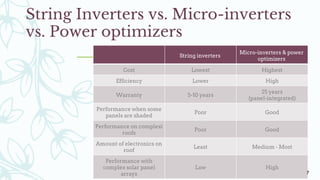
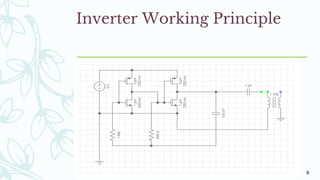
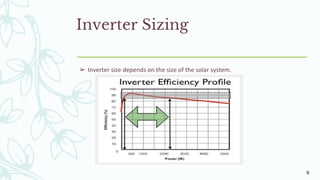
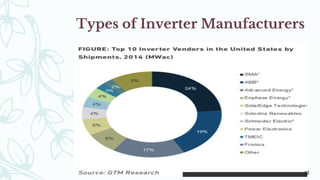
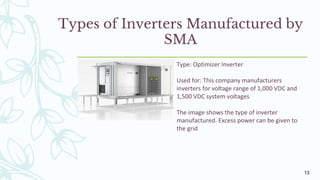
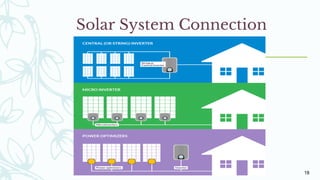
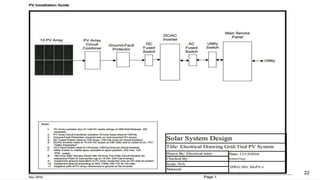
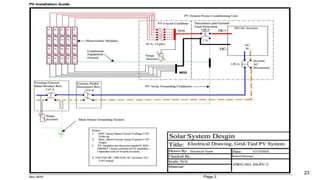
The document provides an overview of solar inverters, including their types, working principles, and sizing considerations for solar energy systems. It discusses string inverters, micro-inverters, and power optimizers, highlighting their cost, efficiency, and performance under shading conditions. Additionally, it outlines key manufacturers and their inverter offerings, along with inverter sizing best practices to optimize system performance.