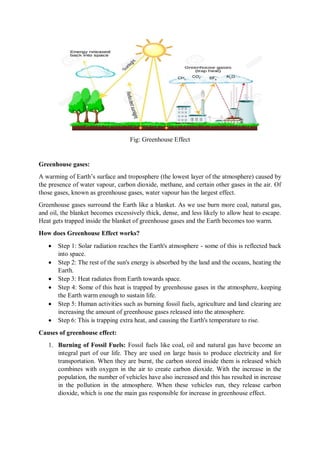
The document discusses the greenhouse effect and global warming, explaining how greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to higher global temperatures. It outlines the causes, including fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and population growth, as well as the consequences such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and threats to biodiversity. To combat these issues, the document emphasizes the importance of reducing emissions, using renewable energy, and promoting ecological awareness.