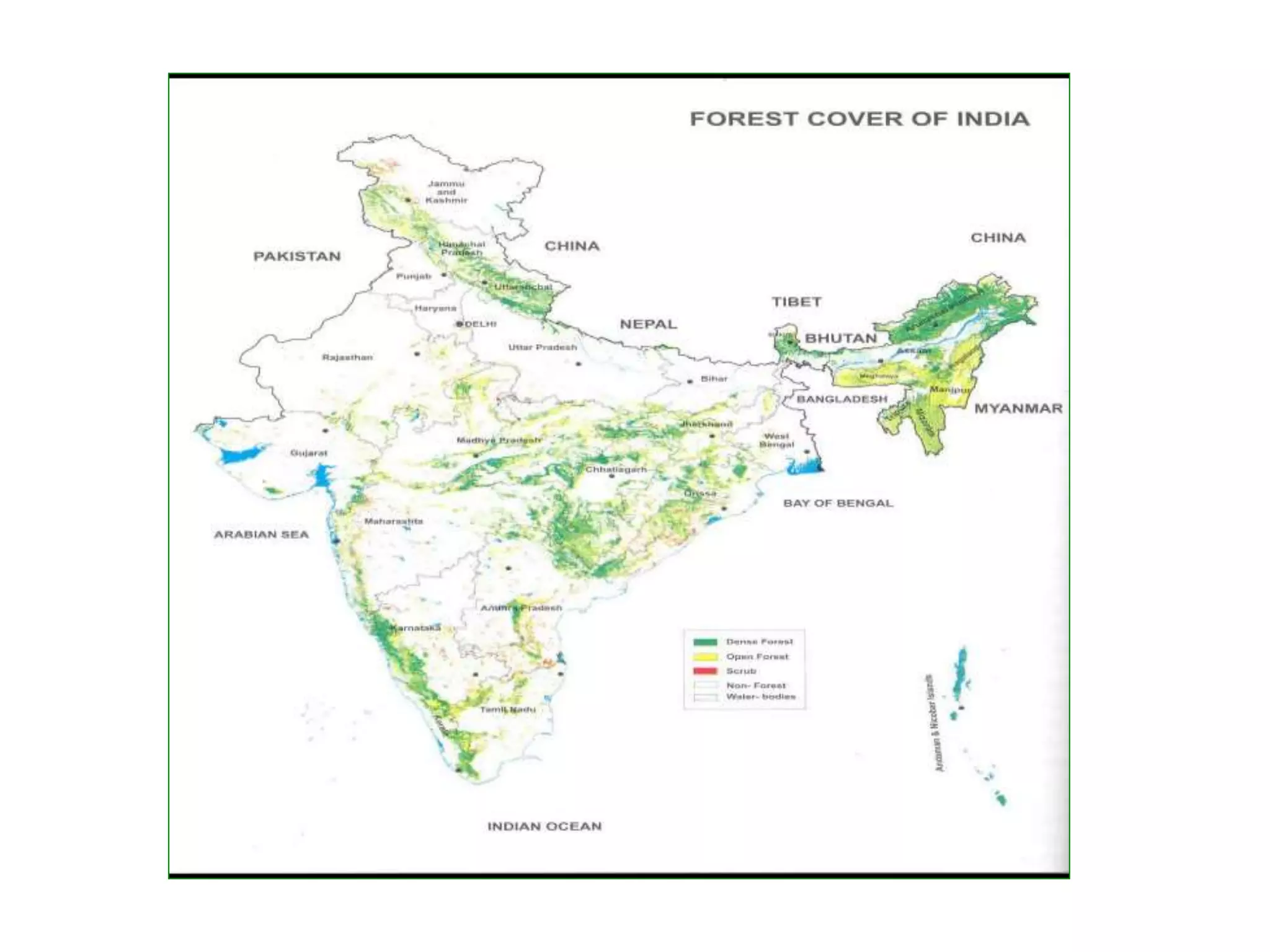
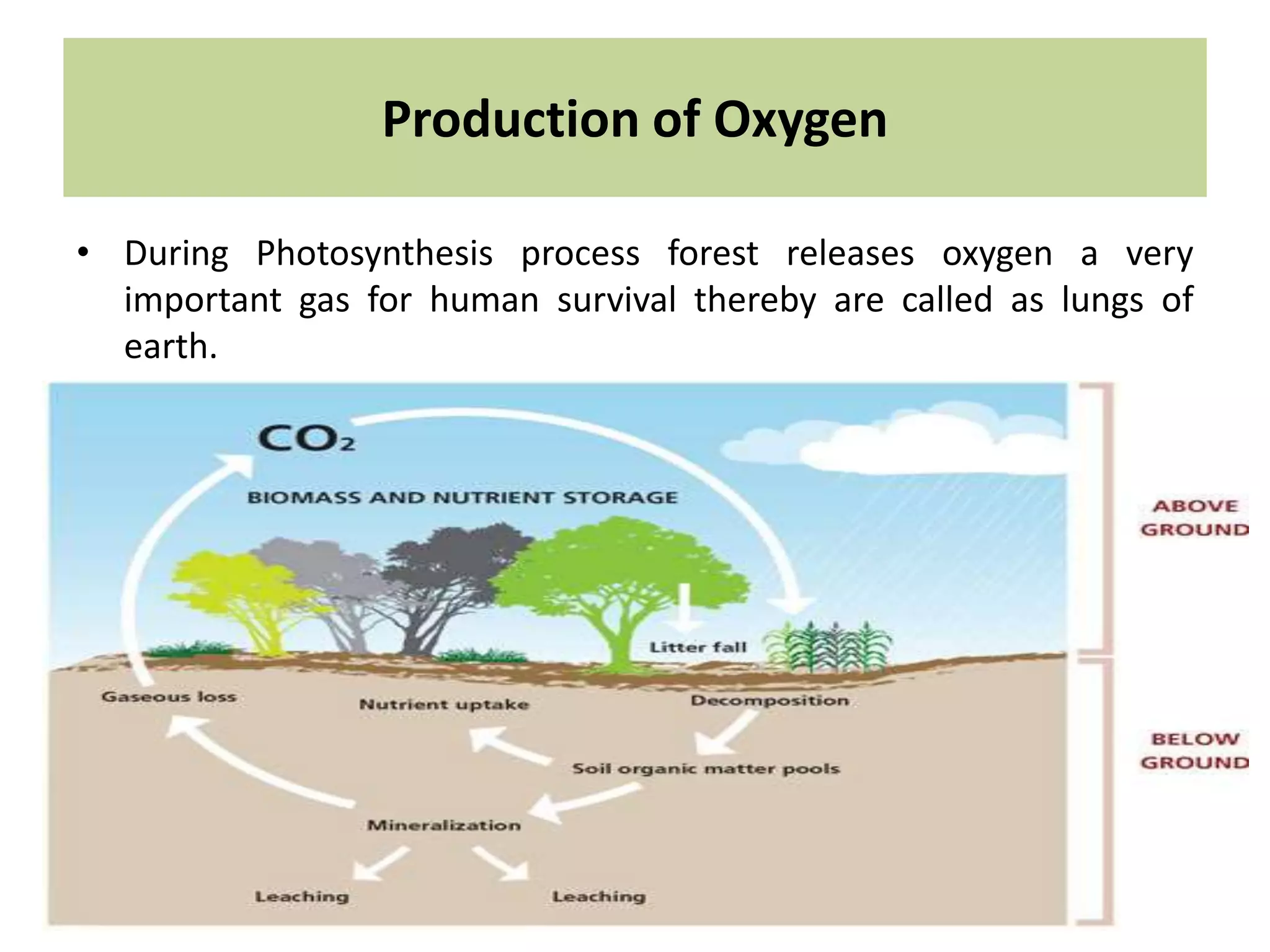
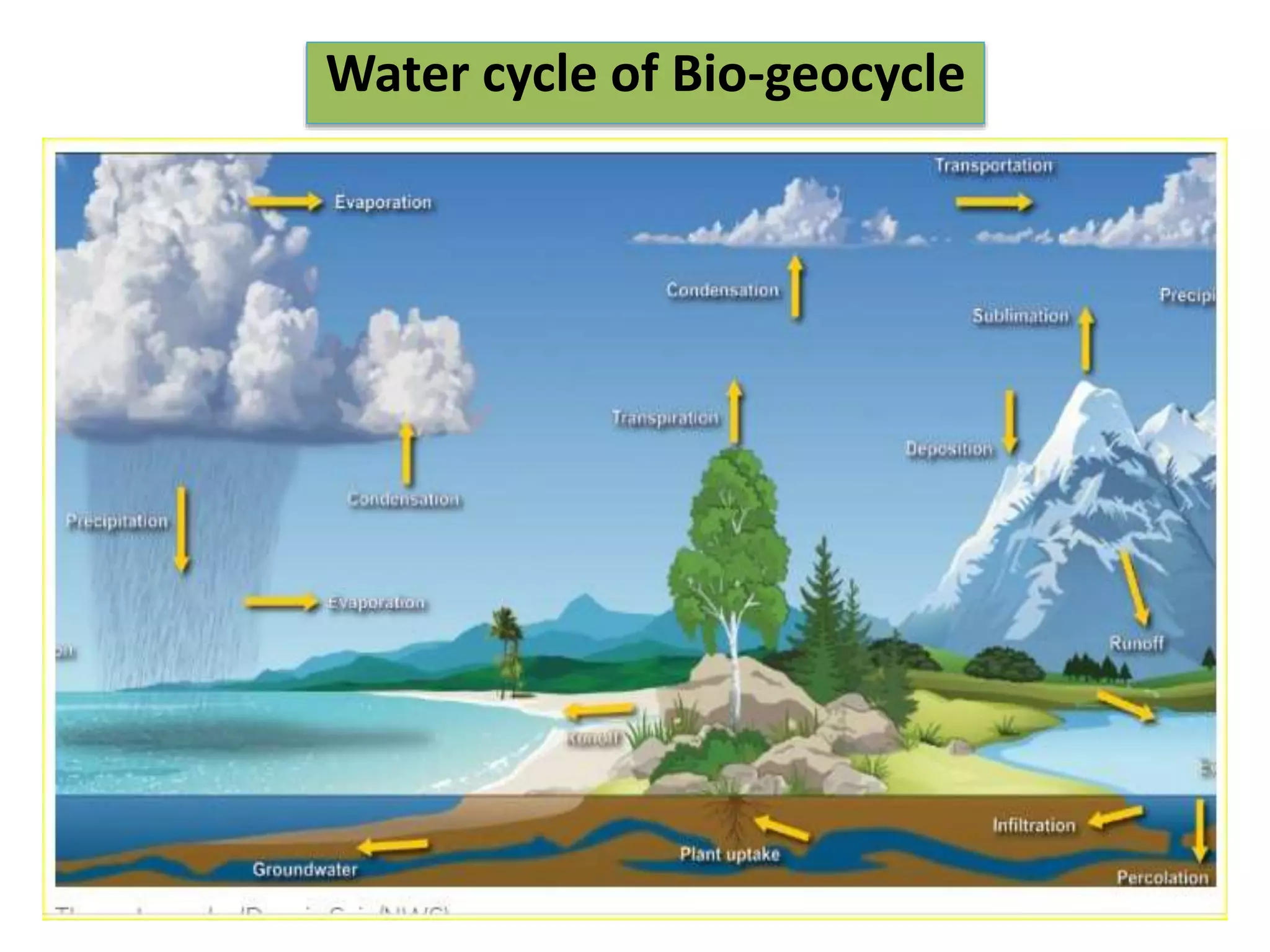
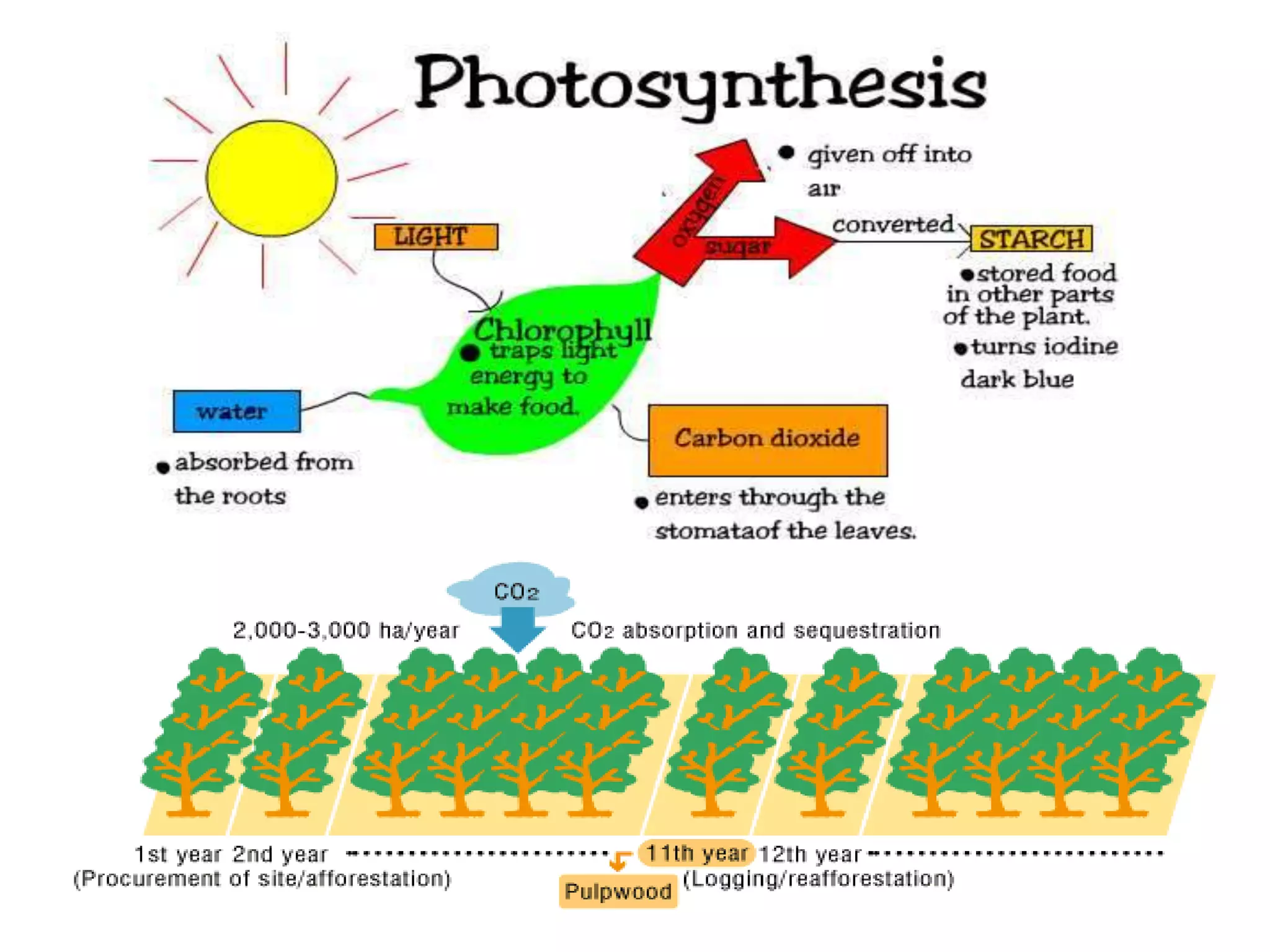
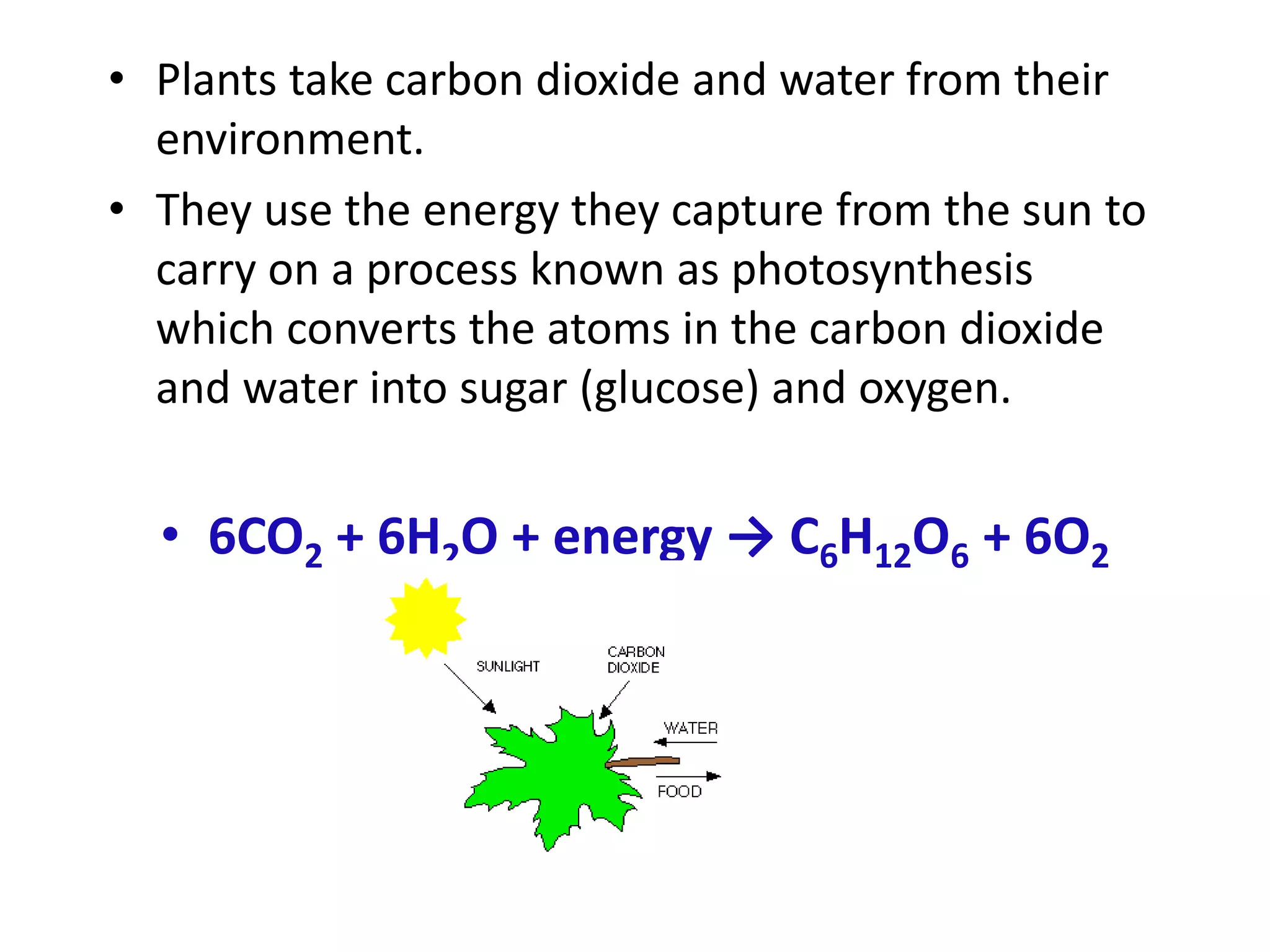
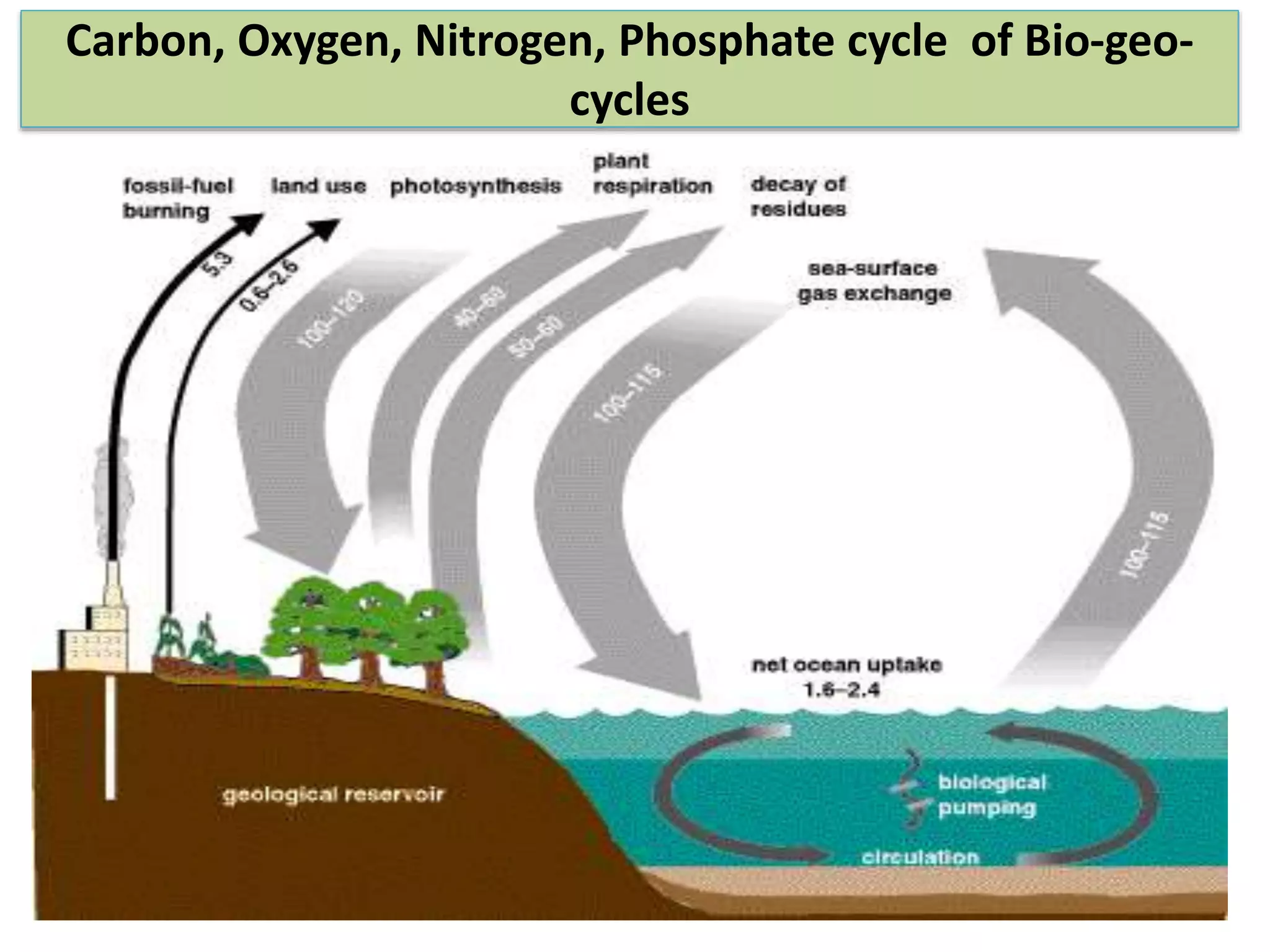
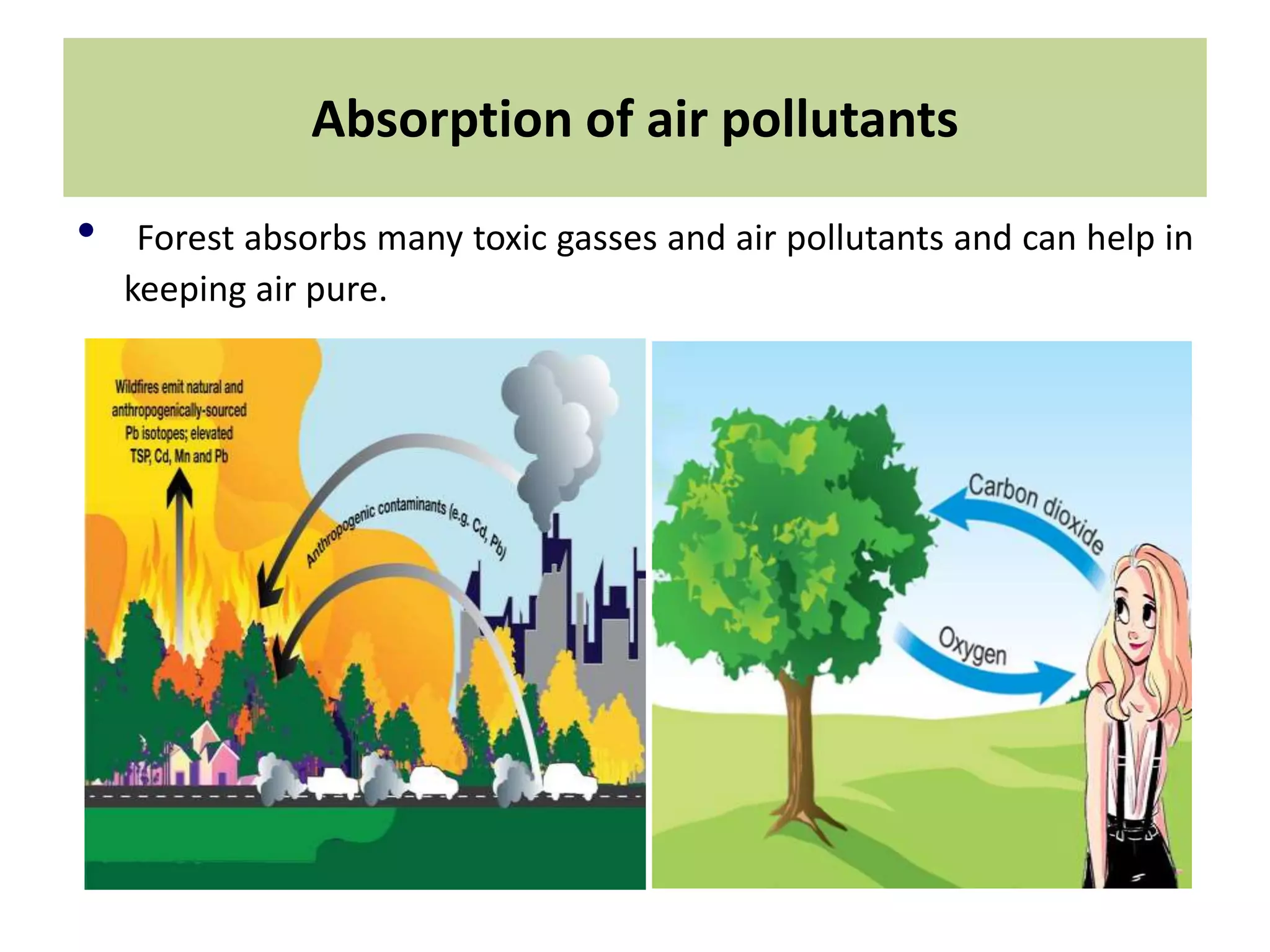
The document discusses the significance of forests and trees in maintaining environmental health, emphasizing their role in providing clean air, water, and biodiversity. It outlines the dangers of deforestation and environmental degradation in India, alongside the need for afforestation and community involvement in restoration efforts. The lecture encourages active participation in the #generationrestoration movement to foster sustainable practices and mitigate climate change.