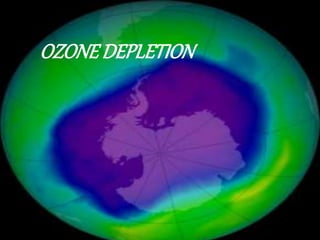
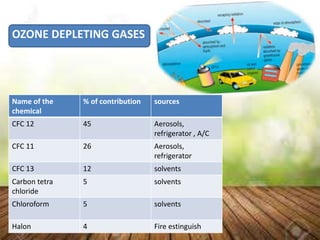
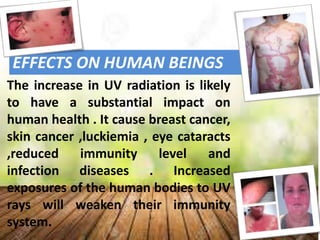
The ozone layer sits 9.3 to 18.6 miles above Earth and shields it from harmful UV radiation. It is formed from ozone, a molecule containing three oxygen atoms that absorbs most UV rays. The ozone layer has been depleted since the 1960s due to gases like CFCs released from aerosols and refrigerants, leading to holes forming. This depletion allows more UV radiation to reach Earth and increases health risks like skin cancer for humans, infections for animals, and decreased crop yields. The 1987 Montreal Protocol aimed to phase out ozone-depleting substances by 2010.