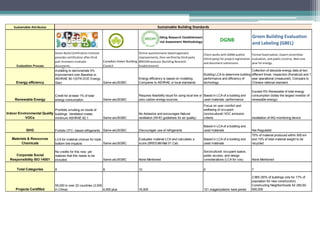
This document provides an overview and comparison of major global green building rating systems including LEED, BREEAM, DGNB, and China's Three Star system and MOHURD standards. It outlines the key sustainable attributes each system evaluates such as energy efficiency, materials and resources, indoor environmental quality, and more. The document also discusses challenges in green building certification including lack of sustainable products and technical expertise as well as the need to decrease resource use and emissions. Finally, it outlines future trends like a focus on renewable energy, zero energy buildings by 2020 in Europe, and the growing importance of corporate social responsibility and people-focused cities.