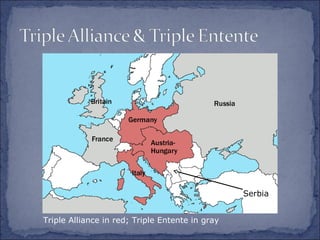
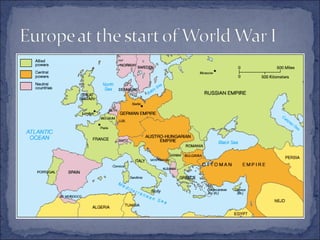
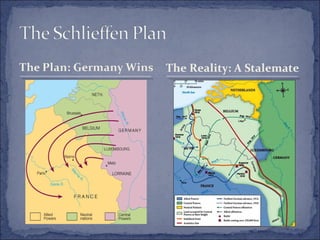
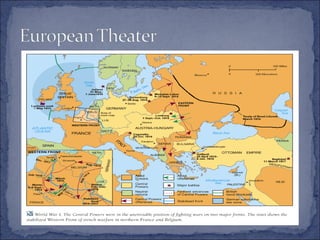
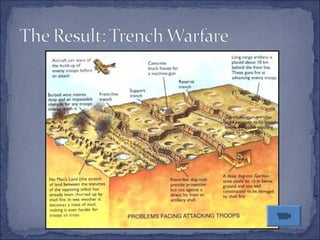
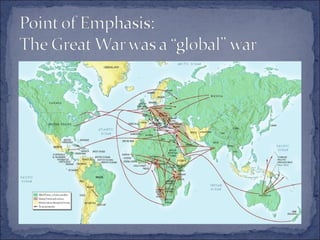
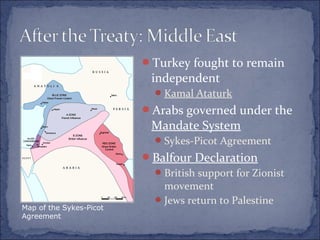
The document summarizes the key events leading up to and during World War 1. It discusses the rise of militarism, imperialism and nationalism in Europe in the late 19th century which increased tensions between the major powers and led to the formation of opposing alliances. The assassination of Archduke Ferdinand in 1914 triggered a series of events that started World War 1. The war became a bloody stalemate using modern industrial warfare techniques across trenches in France and Belgium. It ended in 1918 with the defeat of the Central Powers.