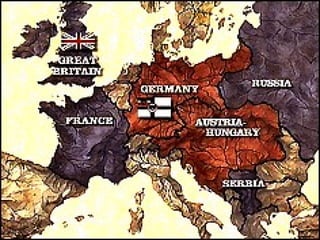
The document provides an overview of World War I, including its long-term and short-term causes, key battles on the Western and Eastern fronts, new military technologies used, America's entry into the war, and how the war was ultimately ended in 1918. Some of the major events and developments discussed include the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand leading to declarations of war across Europe in 1914, the trench warfare and stalemate on the Western Front, America declaring war on Germany in 1917 after attacks on US ships, and Germany agreeing to an armistice in November 1918 to end the war.