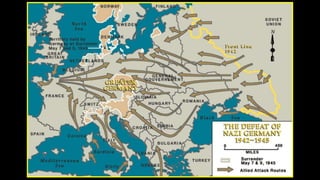
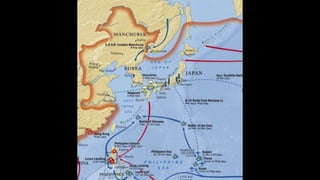
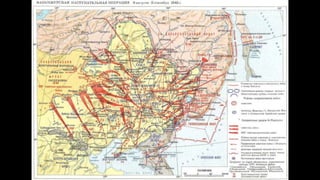
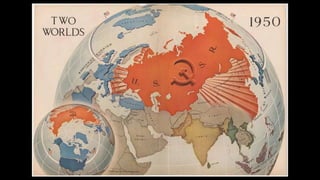
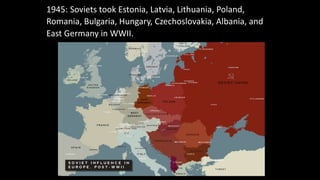
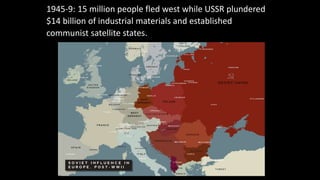
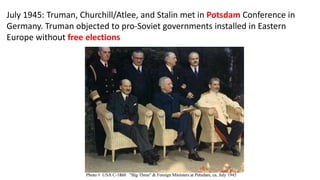
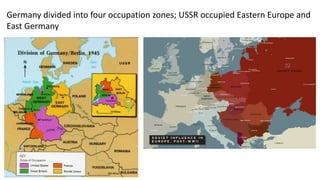
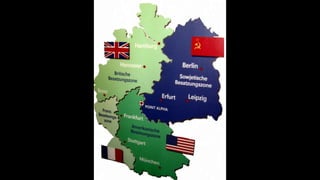
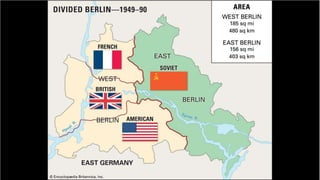
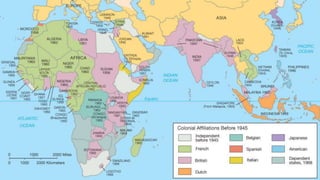
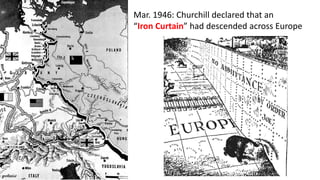
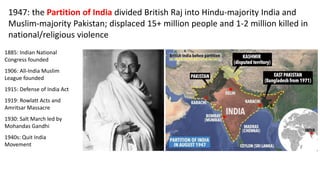
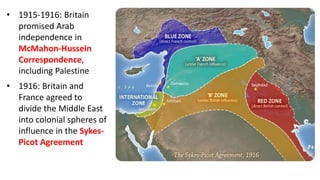
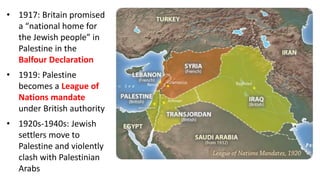
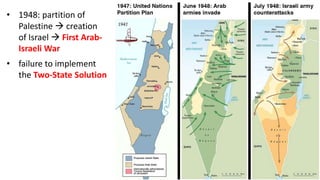
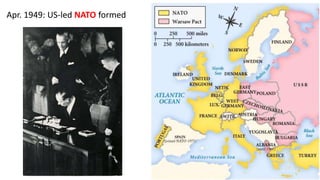
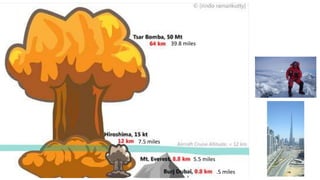
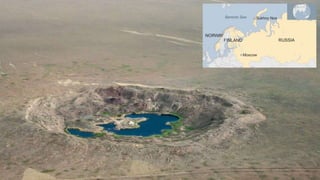
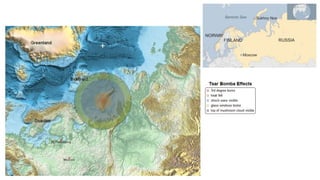
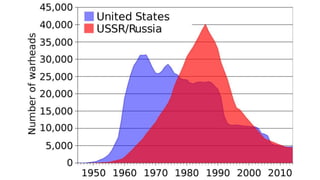
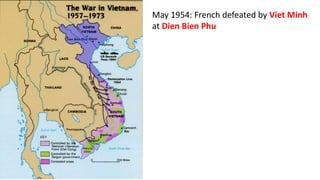
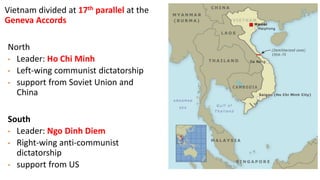
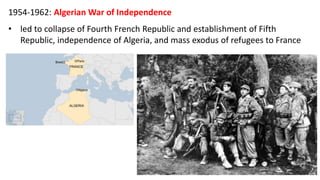
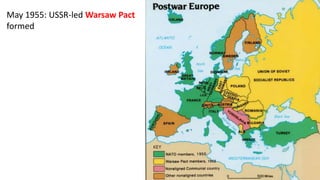
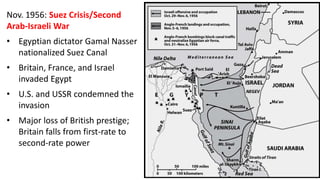
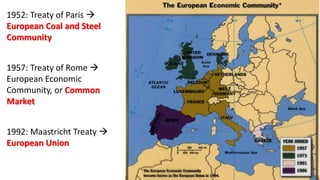
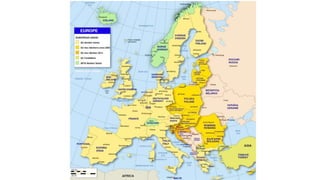
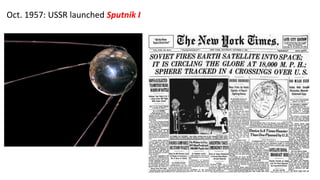
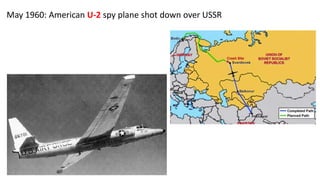
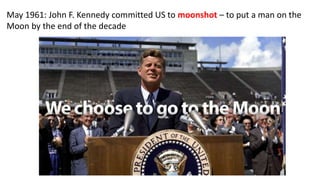
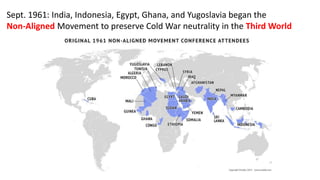
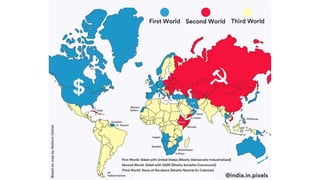
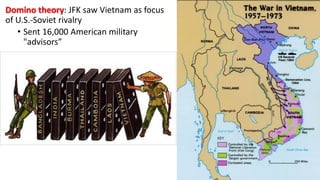
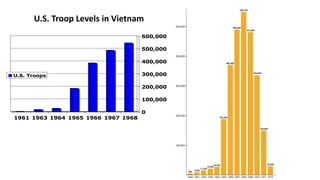
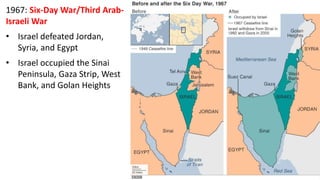
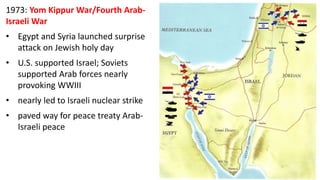
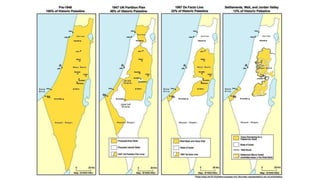
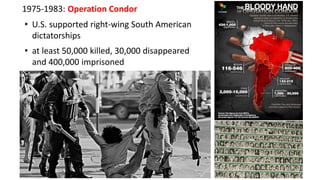
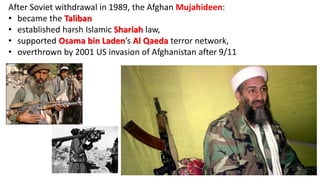
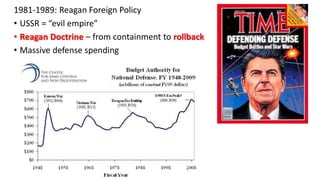
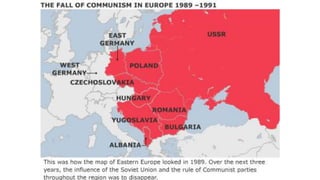
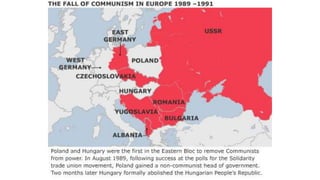
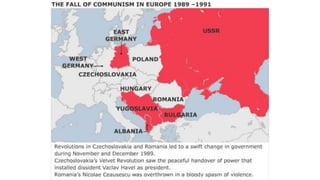
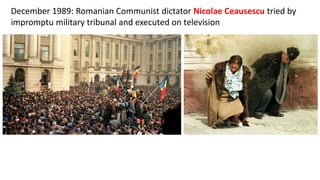
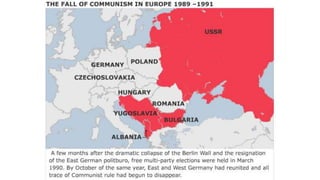
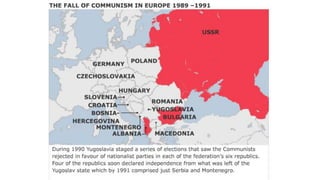
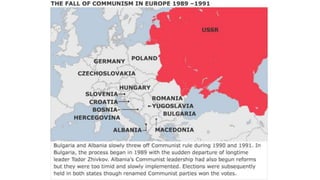
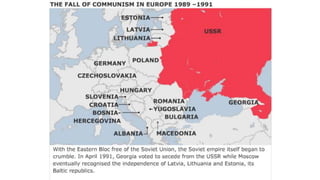
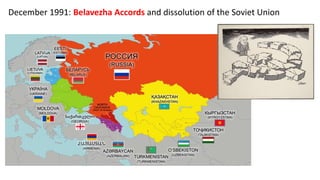
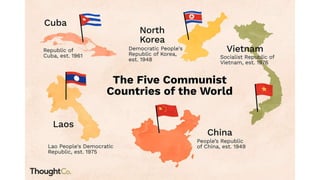
The document provides a detailed overview of major global political and military events from 1945 to 1979 during the Cold War era. Some key developments include: the division of Europe and Germany after WWII; the founding of international organizations like the UN and NATO; decolonization movements and independence struggles across Asia and Africa; conflicts in Korea, Vietnam, and other regions influenced by superpower rivalry; escalating arms races; and periods of both increased tensions and attempts at détente between the U.S. and USSR. The timeline traces the spread of communism and rise of new nations amid ongoing ideological clashes and proxy wars between Western capitalist and Eastern communist blocs during this pivotal period.