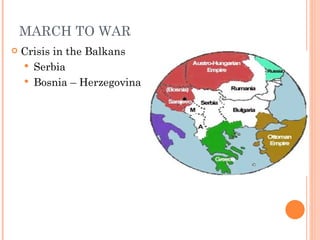
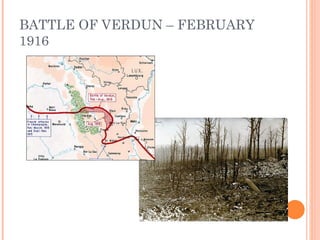
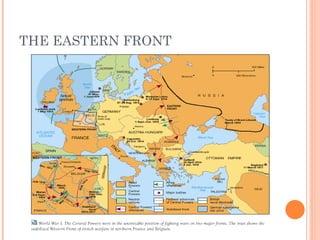
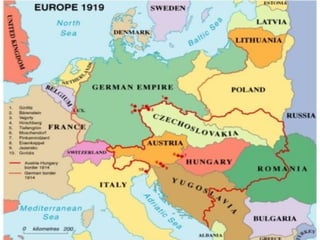
The document summarizes the causes and events of World War 1. It describes the long term tensions between nations including imperialism, militarism and alliances that led to the war. The immediate trigger was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand which set off a chain reaction of countries joining the fighting on both sides. Over 15 million people were killed and societies were fully mobilized for total war until an armistice in 1918 and peace settlement in 1919.