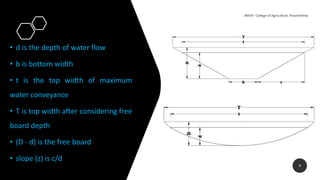
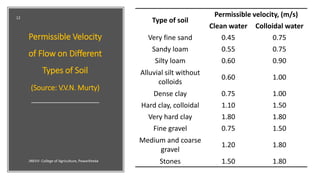
This document discusses the design and construction of grassed waterways. It begins by defining grassed waterways as natural or man-made channels with vegetation cover used to safely transport runoff from fields. It then discusses the purposes of grassed waterways, which include preventing erosion and sedimentation while transporting water. The document provides details on the design process, including calculating dimensions based on watershed characteristics and expected runoff. It recommends shapes, grades, and flow velocities for effective design. Construction and maintenance are also outlined, emphasizing establishing vegetation cover and conducting repairs to ensure proper functioning of grassed waterways over time.