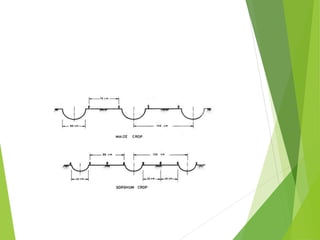
This document discusses various in-situ soil moisture conservation techniques. It introduces the topic and explains that these techniques are recommended in addition to large-scale watershed management structures to increase moisture availability for crops. The techniques aim to increase infiltration and temporarily store water at the soil surface. The document then describes several specific techniques in detail, including deep tillage, mulching, basin listing, broad-based beds and furrows, ridges and furrows, and compartmental bunding. It explains the principles and benefits of each technique for conserving soil moisture.