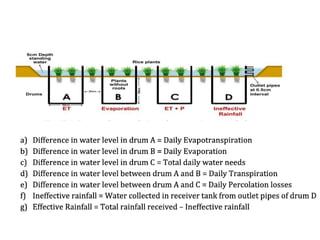
Effective rainfall refers to the portion of total rainfall that is useful for crop production. It is influenced by factors like rainfall amount and intensity, land characteristics like slope and soil type, soil water holding capacity, groundwater levels, and crop water needs. Management practices like bunding and mulching can increase effective rainfall by reducing runoff and improving infiltration. Proper irrigation scheduling allows farmers to apply optimal amounts of water at the right times, maximizing yields while minimizing costs, water use, and damage to soil properties. Common irrigation methods include border, furrow, basin, flood, sprinkler, subsurface, and drip irrigation.