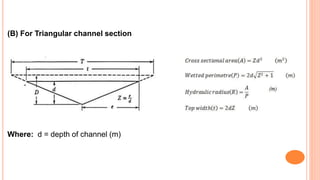
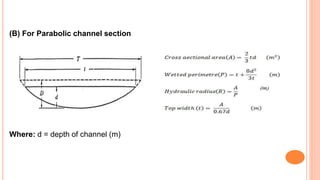
This document discusses grassed waterways, which are natural or man-made channels covered in erosion-resistant grasses that are used to drain surface water from an area. Grassed waterways control soil erosion from runoff by lining the channel with grasses. Their design requires data on watershed characteristics, soil type, and topography to calculate peak runoff rates. Their shape depends on construction equipment availability, flow velocity, grade, and grass cover. Design involves determining peak runoff, assuming a channel cross-section, calculating velocity and capacity using Manning's equation, and iterating assumed dimensions until capacity matches runoff rates.