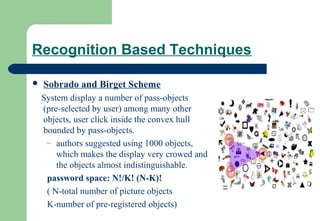
This document discusses graphical passwords as an alternative to alphanumeric passwords. Graphical passwords work by having users select images or points on images in a specific order. They are generally easier for users to remember but harder for others to guess compared to alphanumeric passwords. The document compares graphical and alphanumeric passwords and describes some simple graphical password schemes, advantages like improved security, and disadvantages like longer login times and vulnerability to shoulder surfing. It proposes solutions like triangle-based and movable frame-based schemes to address the shoulder surfing issue.