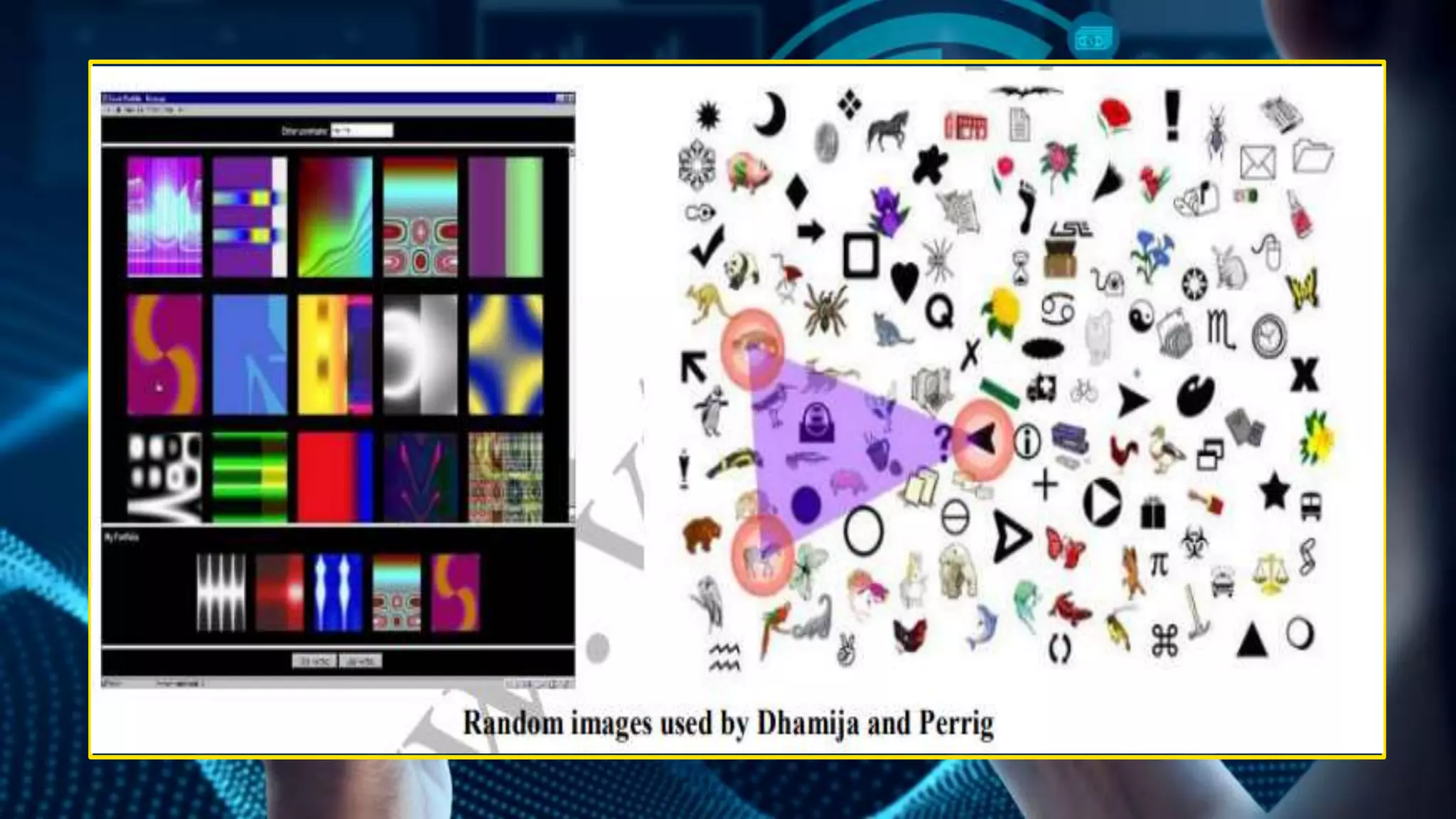
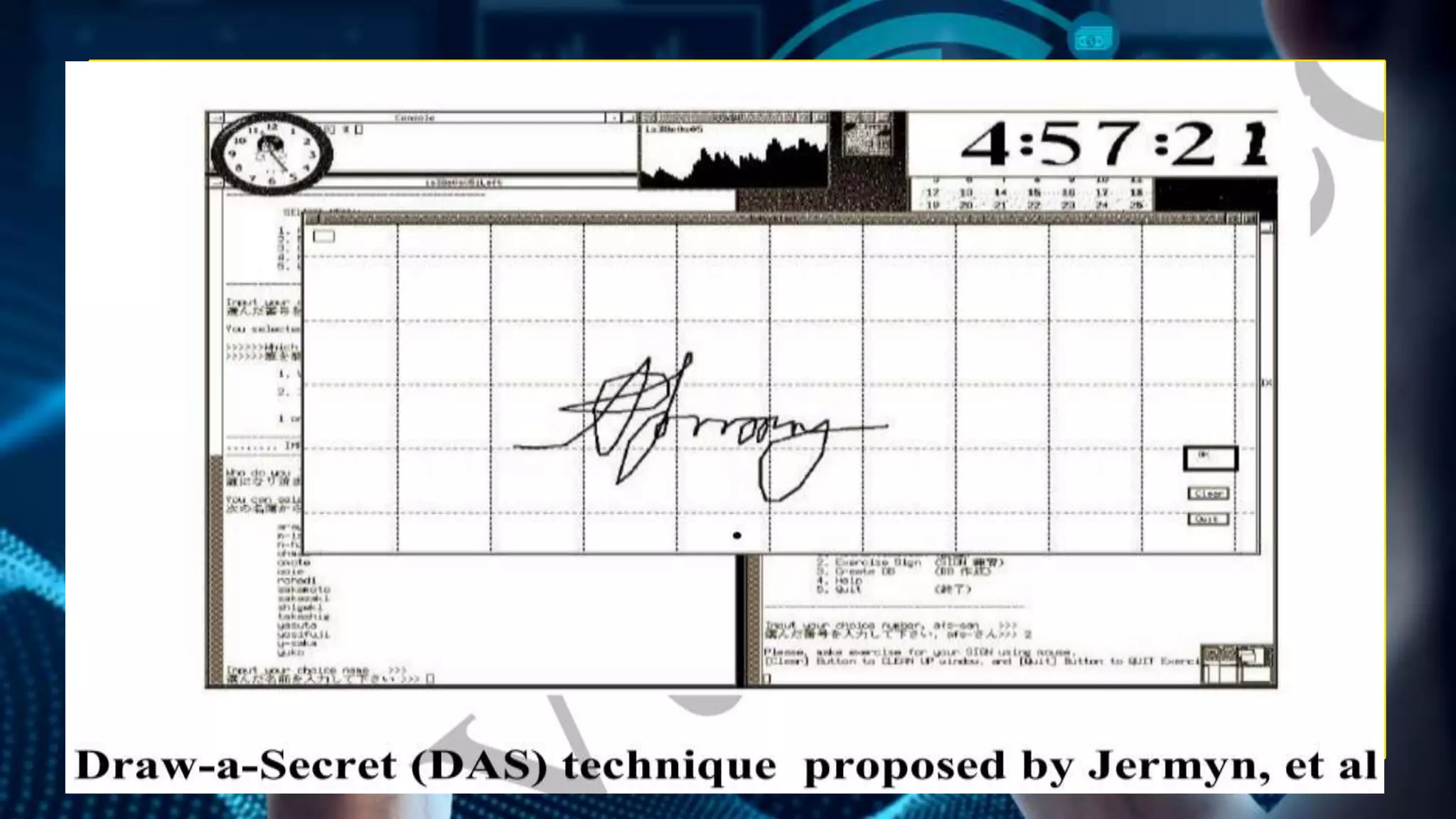
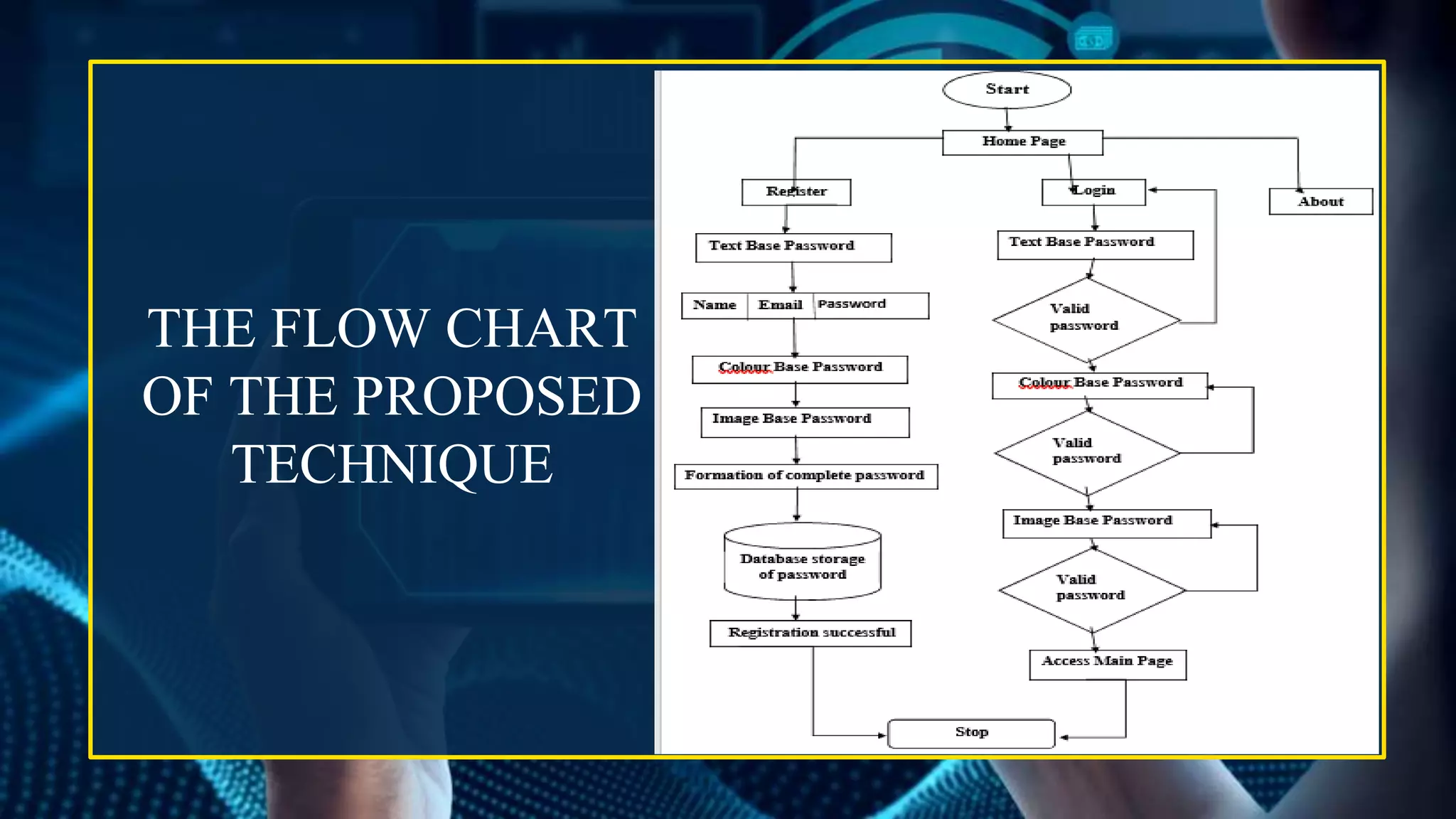
This document provides an overview of graphical password authentication techniques. It begins with an introduction to the limitations of traditional text passwords and an overview of different authentication methods. It then describes recognition-based and recall-based graphical password techniques. A new proposed technique is presented, involving selecting themes or sequences of distorted images. Major design and implementation issues are discussed, such as security, usability, and storage. The document concludes that graphical passwords are an alternative to text passwords but more research is still needed to evaluate their usability and security.
![C. BYRE GOWDA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Department Of Computer Science Engineering
GRAPHICAL PASSWORD AUTHENTICATION
SYSTEM
Staged By : GIRISH K A [ 1CK19CS034 ]
8th Sem , ‘A’ Sec, CSE Dept.
CBIT, KOLAR
Under the Guidance of: KAVITHA N
Asst. Prof. Dept. of CSE
CBIT , KOLAR
Technical Seminar Presentation
On](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/technical-230424155443-cc71691b/75/Technical-pdf-1-2048.jpg)