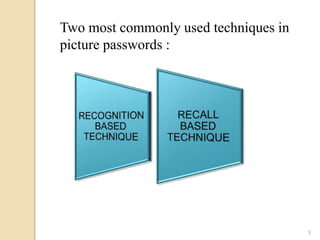
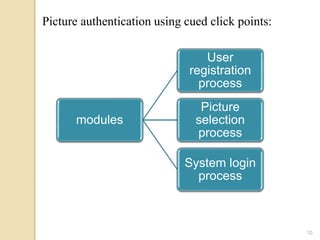
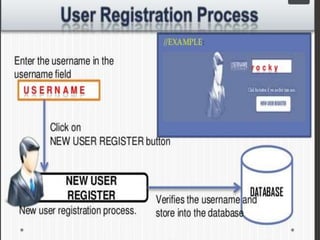
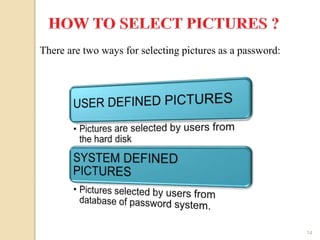
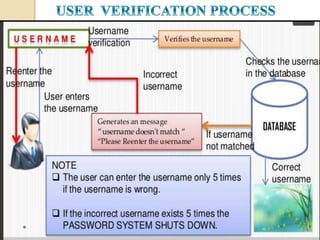
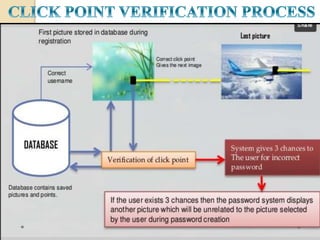
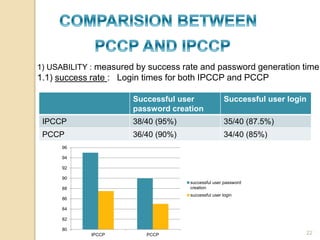
The document discusses various user authentication methods, focusing on graphical passwords, including recognition and recall-based techniques. It evaluates the effectiveness of methods like pass points, cued click points, persuasive cued click points, and improved versions, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages such as the hotspot and shoulder surfing problems. Usability metrics are also presented, showing success rates for different authentication methods.