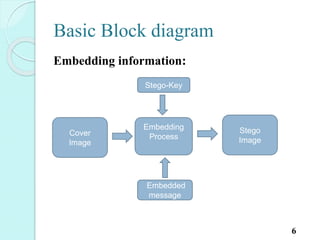
Image steganography is the art of hiding information within digital images. The document discusses various techniques for image steganography including LSB (least significant bit) and DCT (discrete cosine transform). LSB is a simple spatial domain technique that replaces the least significant bits of image pixels with bits of a secret message. DCT operates in the frequency domain by transforming image blocks and hiding data in the mid-frequency DCT coefficients. The document compares the advantages and disadvantages of these techniques, and discusses their applications for hiding private information or digital watermarking. Metrics for analyzing steganography systems like bit error rate, mean square error, and peak signal to noise ratio are also introduced.





![Different Techniques[1]
There are two categories:
1)Spatial Domain:
which mainly includes LSB(Least
Significant Bit)
2)Frequency Domain:
which includes DCT(Discrete cosine
transform) and Wavelet Transform.
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-i-150824154213-lva1-app6892/85/Image-steganography-9-320.jpg)
![Least Significant Bit
Simple approach to embedding information in
a cover image.
It operates on principle that the human eye can
not differentiate between two shade separated by
only one bit.
Algorithm to embed the message:[1]
Read the cover image and text message which is
to be hidden in the cover image.
Convert the color image into grey image.
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-i-150824154213-lva1-app6892/85/Image-steganography-10-320.jpg)



![Process of DCT based image
Steganography are as follow:[2]
Embedding information:
Load cover image and secret image.
Divide the cover image in to 8x8 blocks of
pixels.
Transform the cover image from spatial domain
to frequency using two dimensional DCT .
Quantize the DCT coefficients by dividing using
factor in to the rounded value. 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-i-150824154213-lva1-app6892/85/Image-steganography-16-320.jpg)
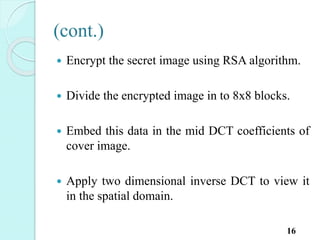
![Block Diagram of DCT[2]
secret
message
17
Encryptio
n
Embeddi
ng
2D DCT
on each
block
8*8 block
preparatio
n
Cover
image
2D IDCT
on each
block
Stego
Embedding information:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-i-150824154213-lva1-app6892/85/Image-steganography-18-320.jpg)
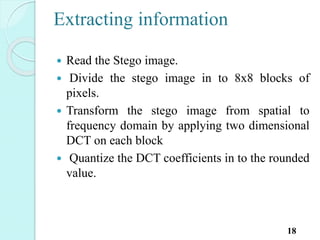
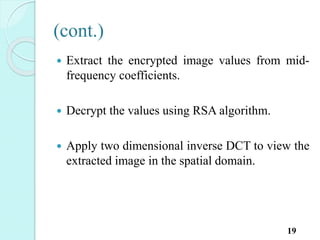
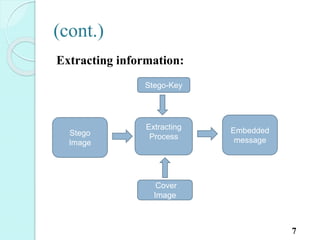
![Extracting information[2]
20
Stego
image
8*8 block
preparatio
n
2D DCT
on each
block
Extraction
2D IDCT
on each
block
Decryptio
n
Extracted
image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-i-150824154213-lva1-app6892/85/Image-steganography-21-320.jpg)



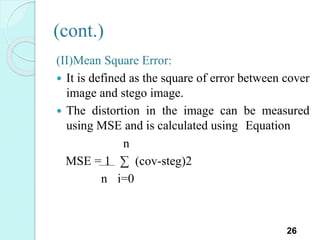
![Error Analysis [2]
(I)Bit Error Rate(BER):
For the successful recovery of the hidden
information the communication channel must be
ideal.
for the real communication channel, there will
be error while retrieving hidden information and
this is measured by BER.
all pixel
BER= 1 ∑ |image cov -image steg |
|image cov| i=0
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-i-150824154213-lva1-app6892/85/Image-steganography-26-320.jpg)