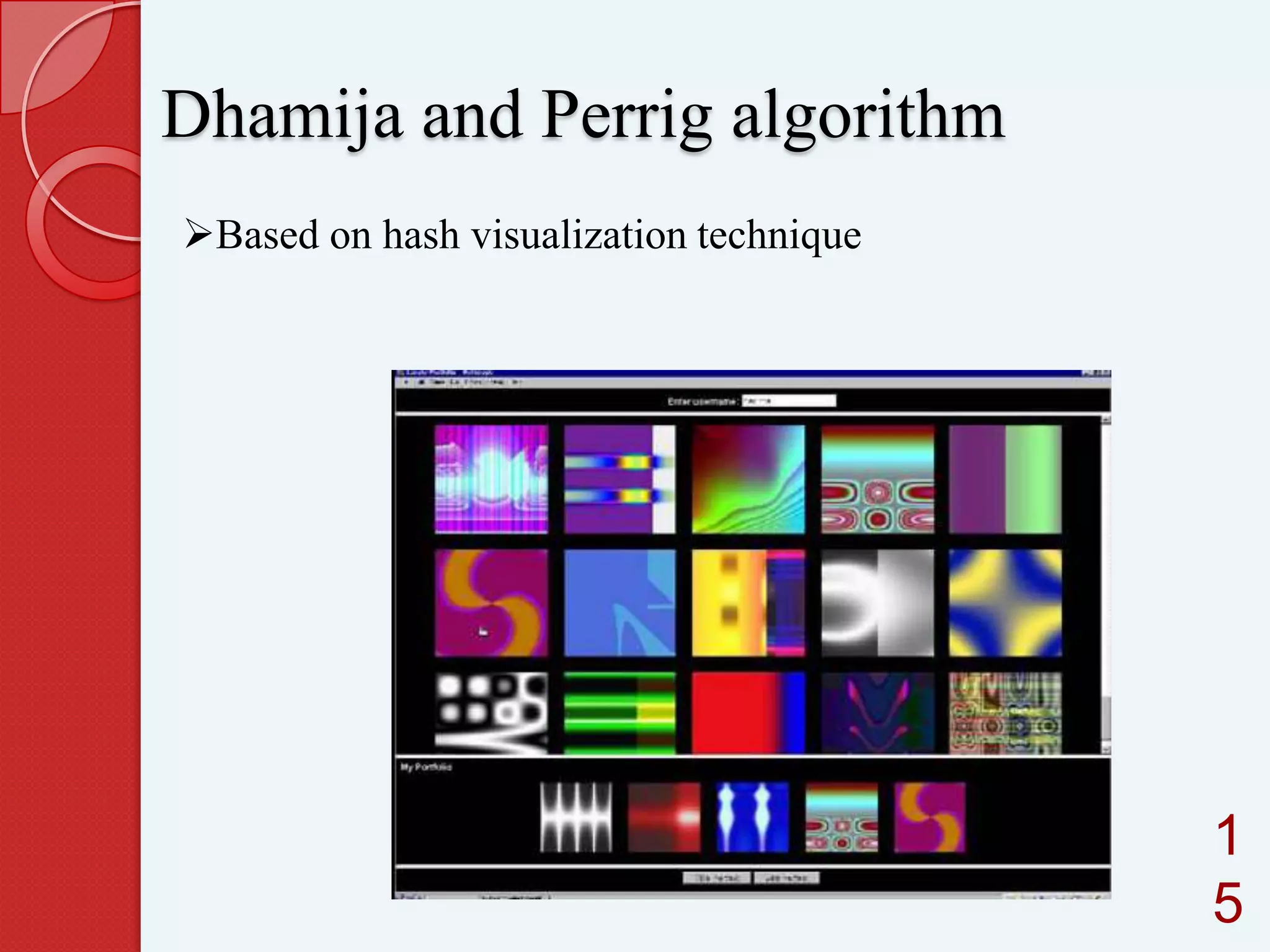
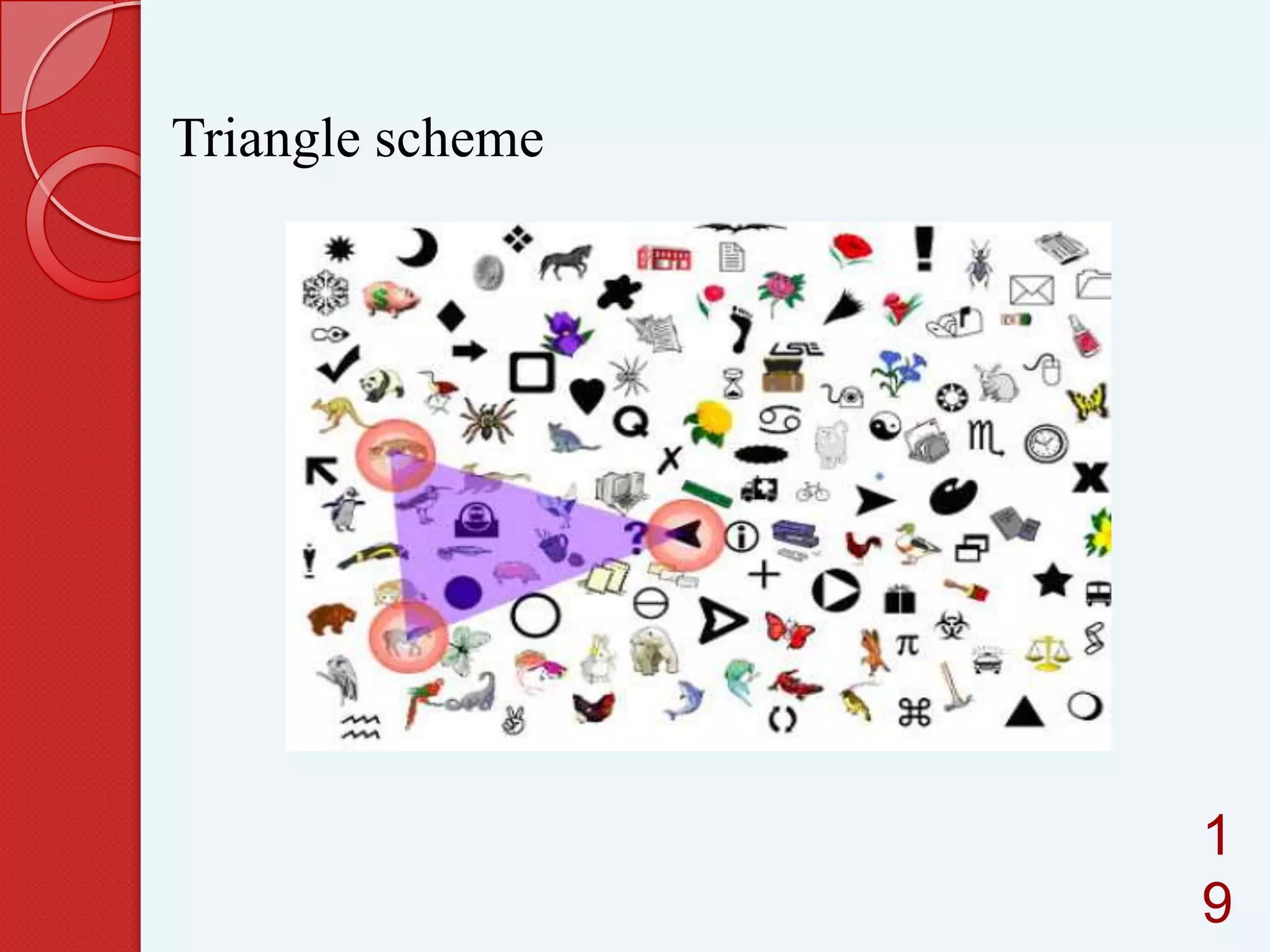
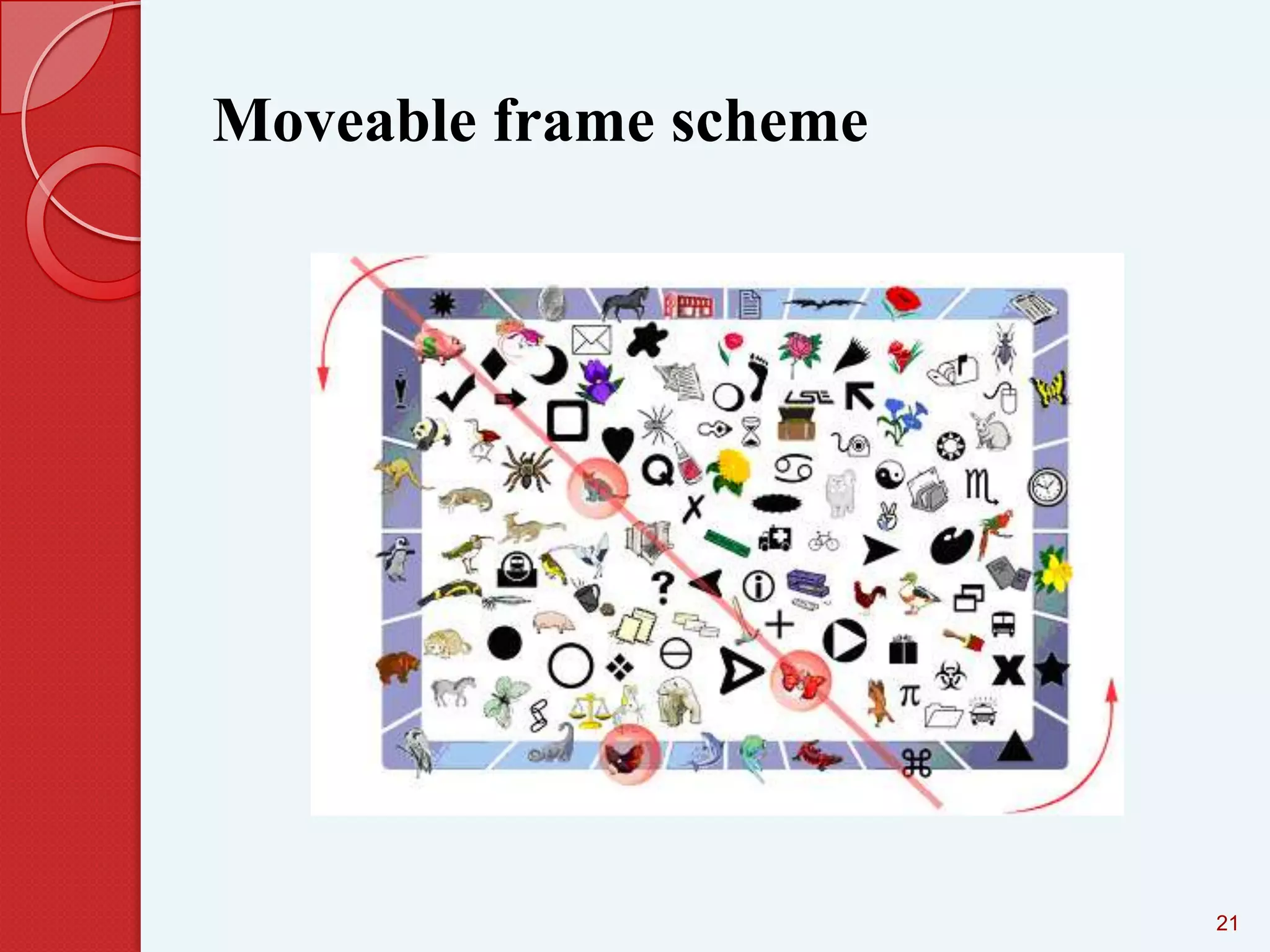
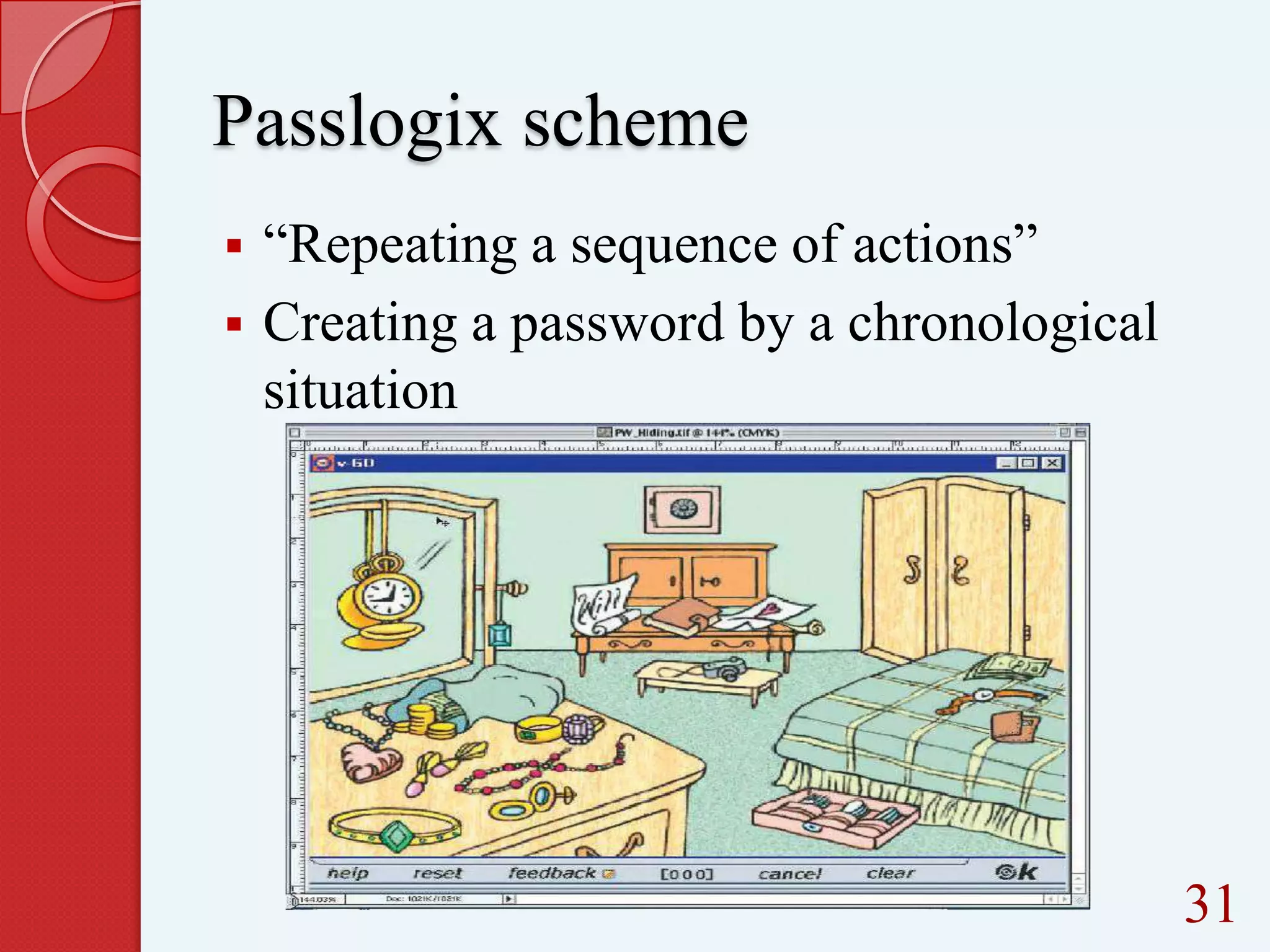
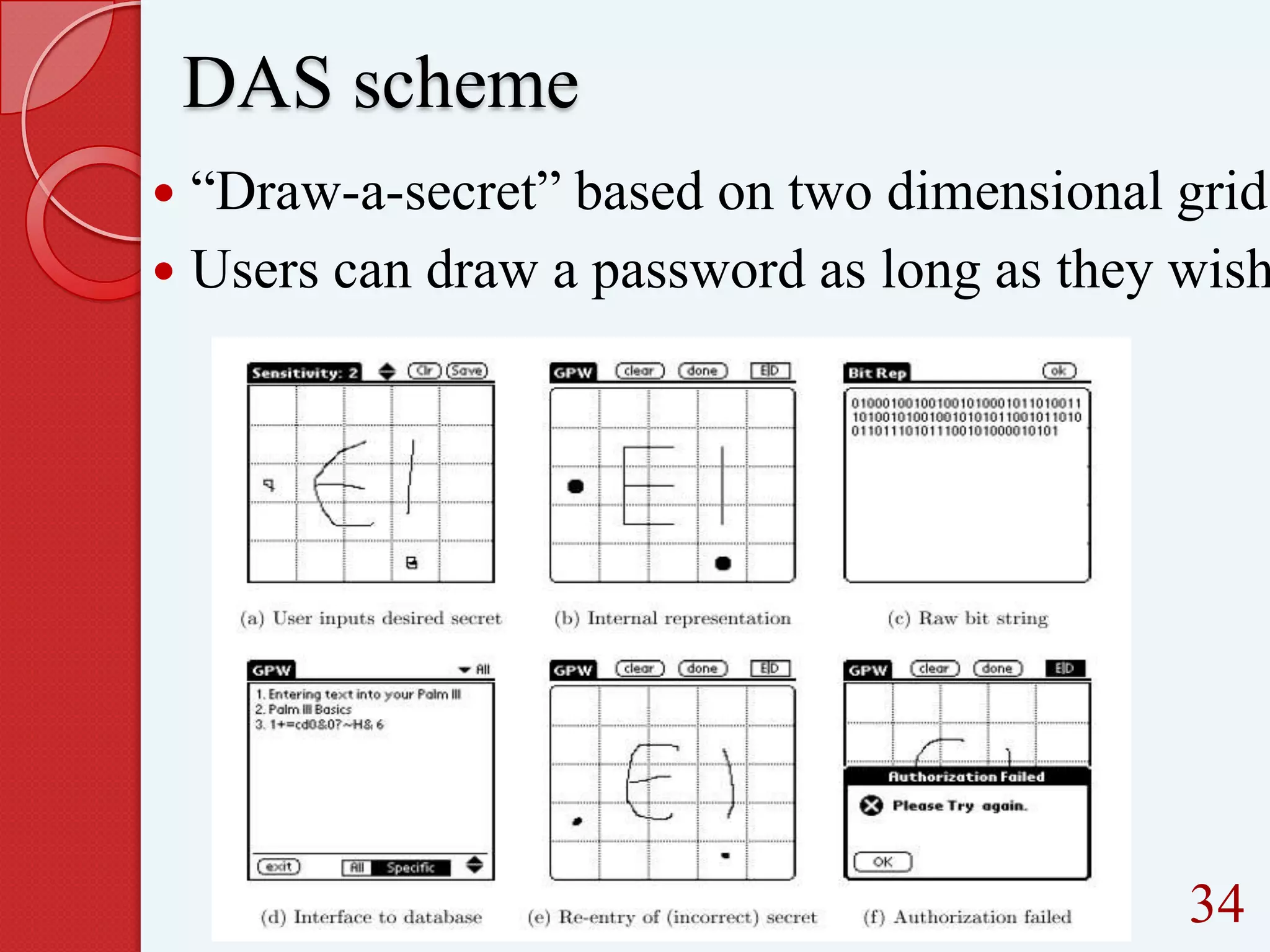
This document summarizes and compares different graphical password authentication methods. It begins by outlining current authentication methods like tokens, biometrics, and text passwords before discussing the drawbacks of text passwords. It then introduces graphical passwords as a more memorable and secure alternative. The document divides graphical passwords into two categories: recognition-based techniques, where users identify previously selected images, and recall-based techniques, where users reproduce a previous action. Several recognition and recall techniques are then described in detail, including their advantages and disadvantages. The document concludes that graphical passwords are more difficult to crack than traditional text passwords.