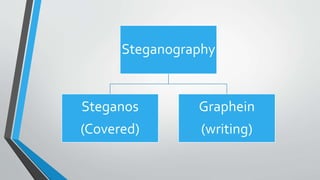
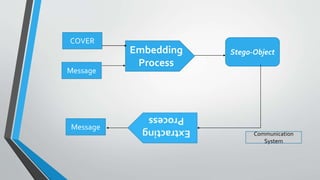
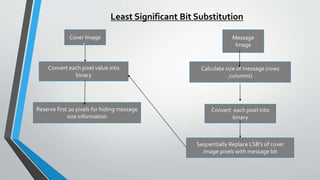
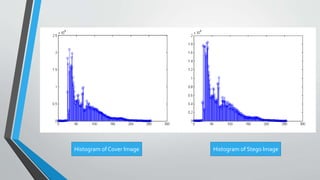
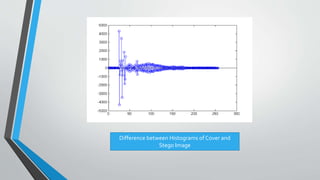
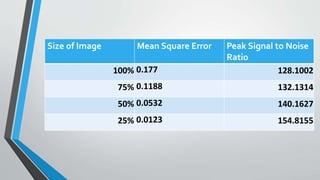
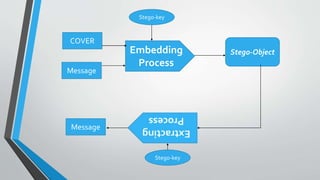
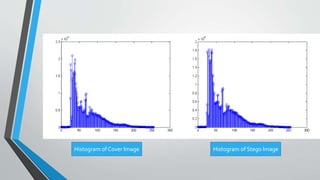
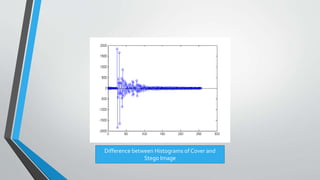
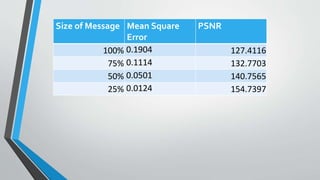
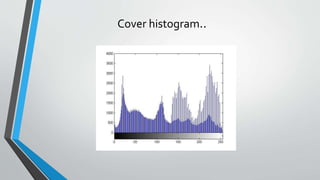
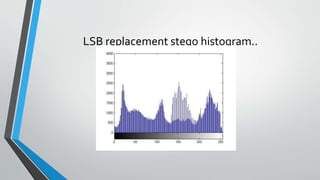
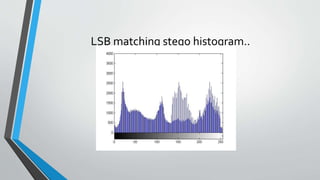
The document discusses image steganography techniques. It begins by defining steganography as concealed writing and distinguishing it from cryptography. It then describes the basic process of embedding a secret message into a cover image to produce a stego-image. Different embedding algorithms are presented, including Least Significant Bit substitution and LSB with randomization. Histograms are used to analyze the differences between cover and stego-images. The document concludes by discussing attackers and techniques to improve robustness, such as LSB matching and Mielikainen's improved LSB matching method.