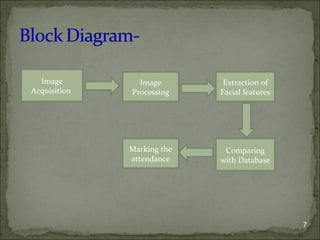
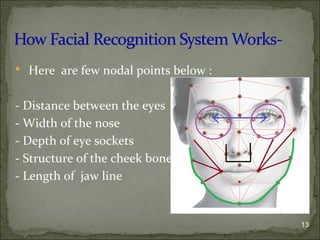
The document discusses the implementation of facial recognition technology as a biometric solution for automated attendance systems in classrooms, highlighting its efficiency compared to traditional manual methods. It outlines the stages of implementation, including image acquisition, processing, and feature comparison, while emphasizing the technology's accuracy and potential applications in various sectors like security and healthcare. Additionally, it mentions important features and nodal points used in facial recognition to improve identification and verification processes.