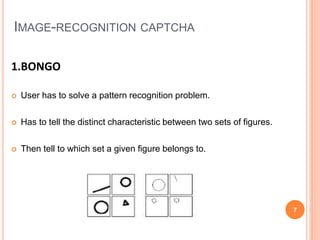
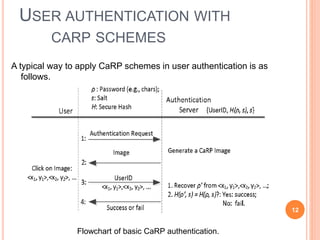
This document proposes a new type of graphical password system called CAPTCHA As Graphical Passwords (CaRP) that integrates CAPTCHAs with password authentication. CaRP schemes require users to click on a sequence of visual objects like characters, animals or grid cells in an image to enter their password. This combines the tasks of recognizing CAPTCHA objects and recalling a click-sequence password. CaRP aims to thwart automatic guessing attacks by generating new images for each login attempt. Recognition-based CaRP examples include Click Text and Click Animal, while Animal Grid combines recognition and cued recall. CaRP is resistant to relay attacks and provides stronger security than other graphical passwords by leveraging hard AI problems in CAPT


















![REFERENCES
[1] Bin B. Zhu, Jeff Yan, Guanbo Bao, Maowei Yang, and Ning Xu “Captcha as
Graphical Passwords—A New Security Primitive Based on Hard AI Problems”
VOL. 9, NO. 6, JUNE 2014
[2] R. Biddle, S. Chiasson, and P. C. van Oorschot, “Graphical passwords:
Learning from the first twelve years,” ACM Compute Surveys, vol. 44, no. 4,
2012.
[3] I. Jermyn, A. Mayer, F. Monrose, M. Reiter, and A. Rubin, “The design and
analysis of graphical passwords,” in Proc. 8th USENIX Security Symp., 1999,
pp. 1–15.
[4] H. Tao and C. Adams, “Pass-Go: A proposal to improve the usability of
graphical passwords,” Int. J. Netw. Security , vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 273– 292, 2008.
[5] S. Wiedenbeck, J. Waters, J. C. Birget, A. Brodskiy, and N. Memon,
“PassPoints: Design and longitudinal evaluation of a graphical password
system,” Int. J. HCI, vol. 63, pp. 102–127, Jul. 2005.
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/captchaasgraphicalpassword-150111225209-conversion-gate02/85/Captcha-as-graphical-password-21-320.jpg)
