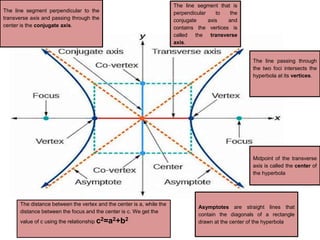
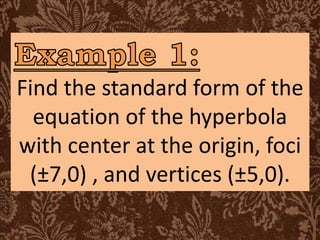
This document defines key terms related to hyperbolas and provides examples of finding the standard form of the equation of a hyperbola given certain properties. It defines a hyperbola as a set of points where the absolute difference between the distances to two fixed points (foci) is a constant. It provides examples of identifying the vertices, foci, asymptotes, and standard form of the equation from information given, such as the coordinates of vertices and foci or the asymptotes.