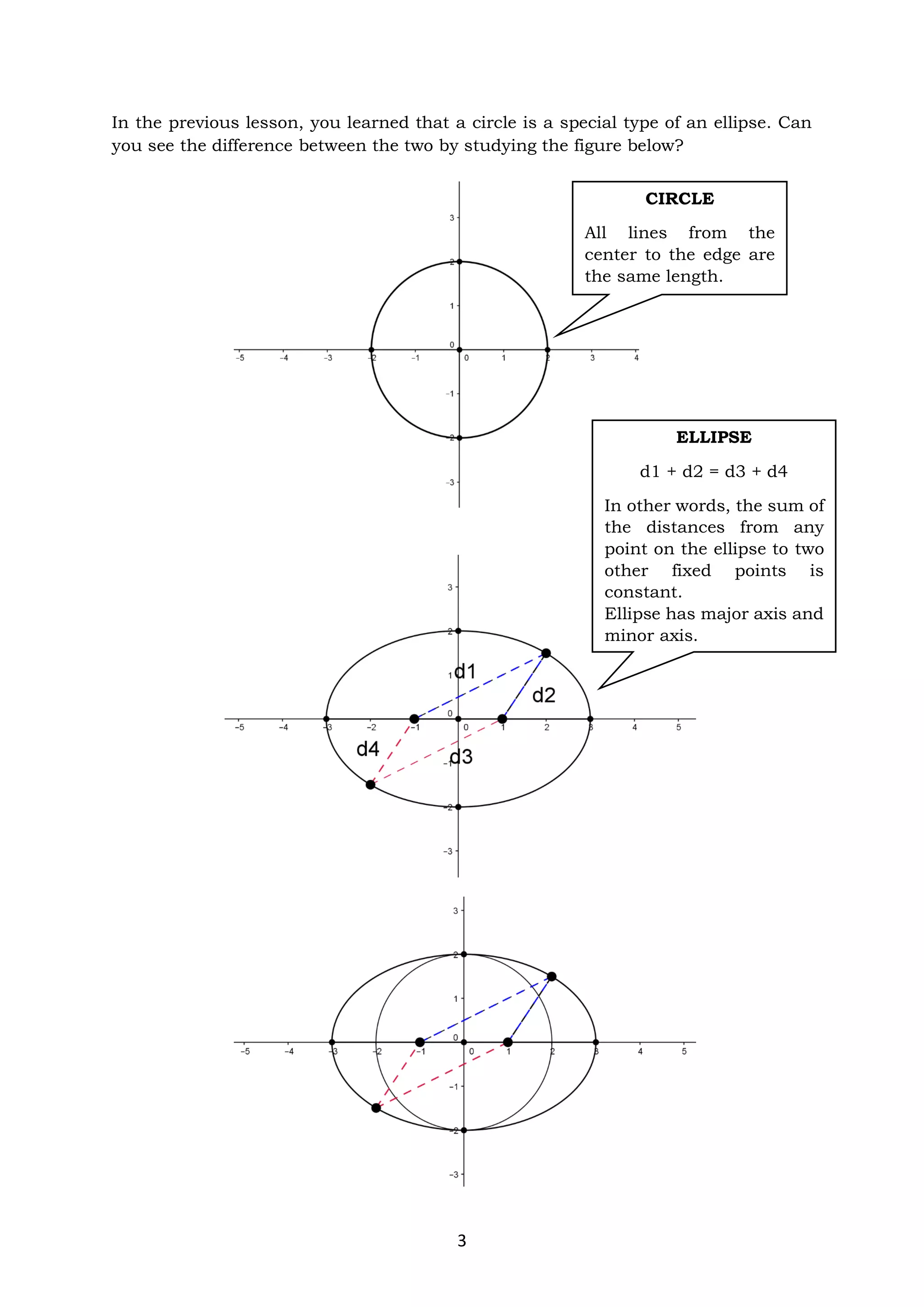
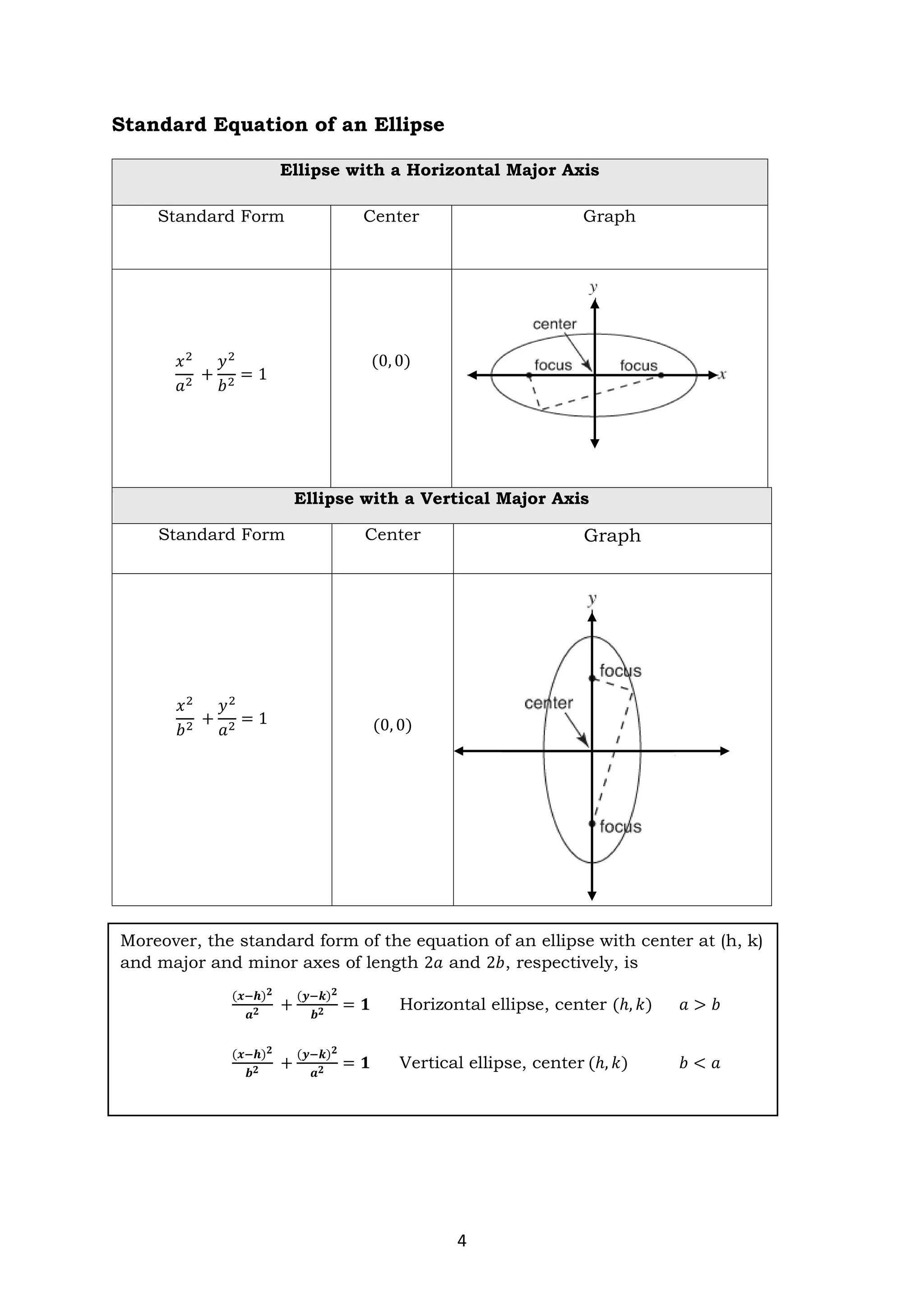
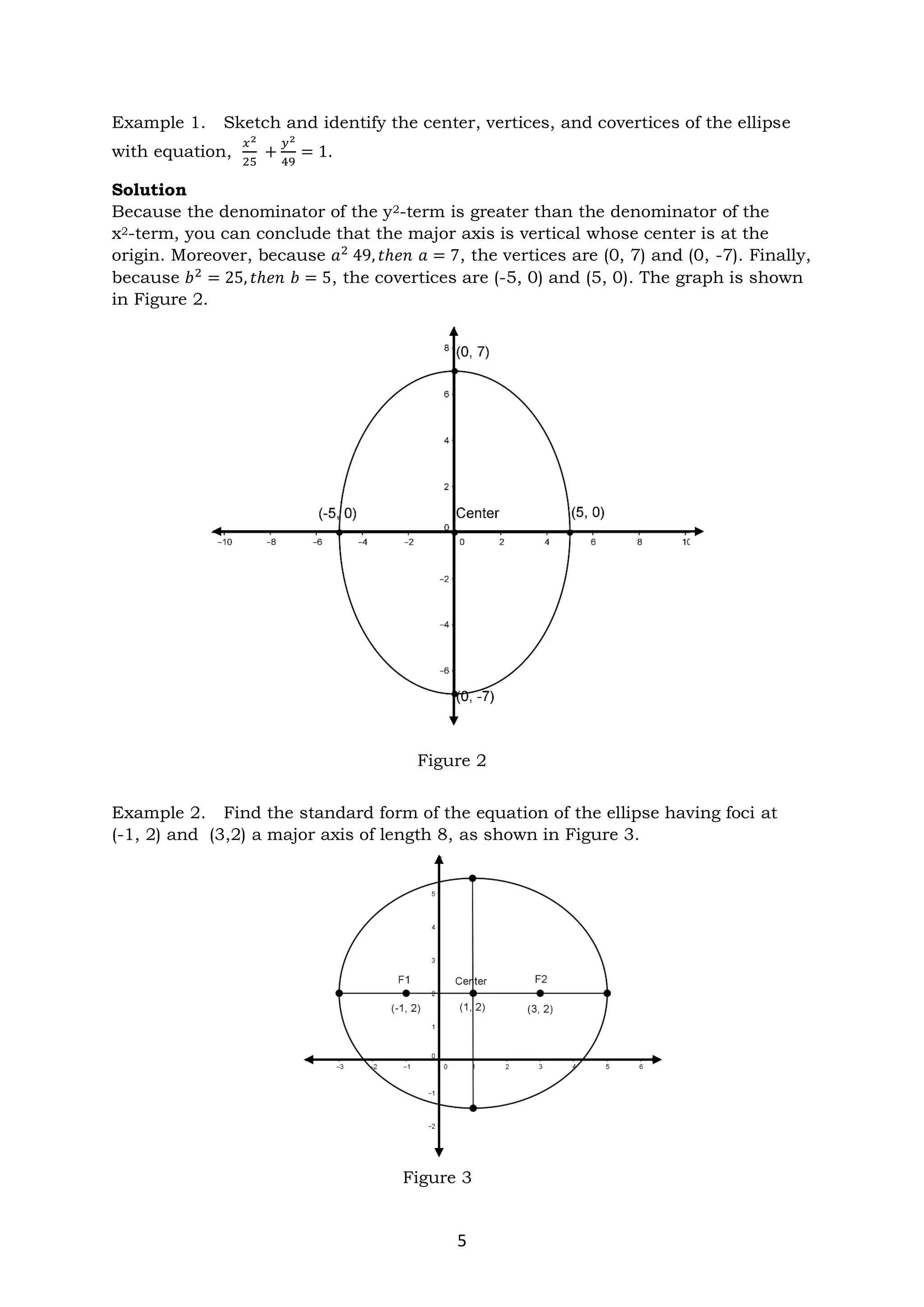
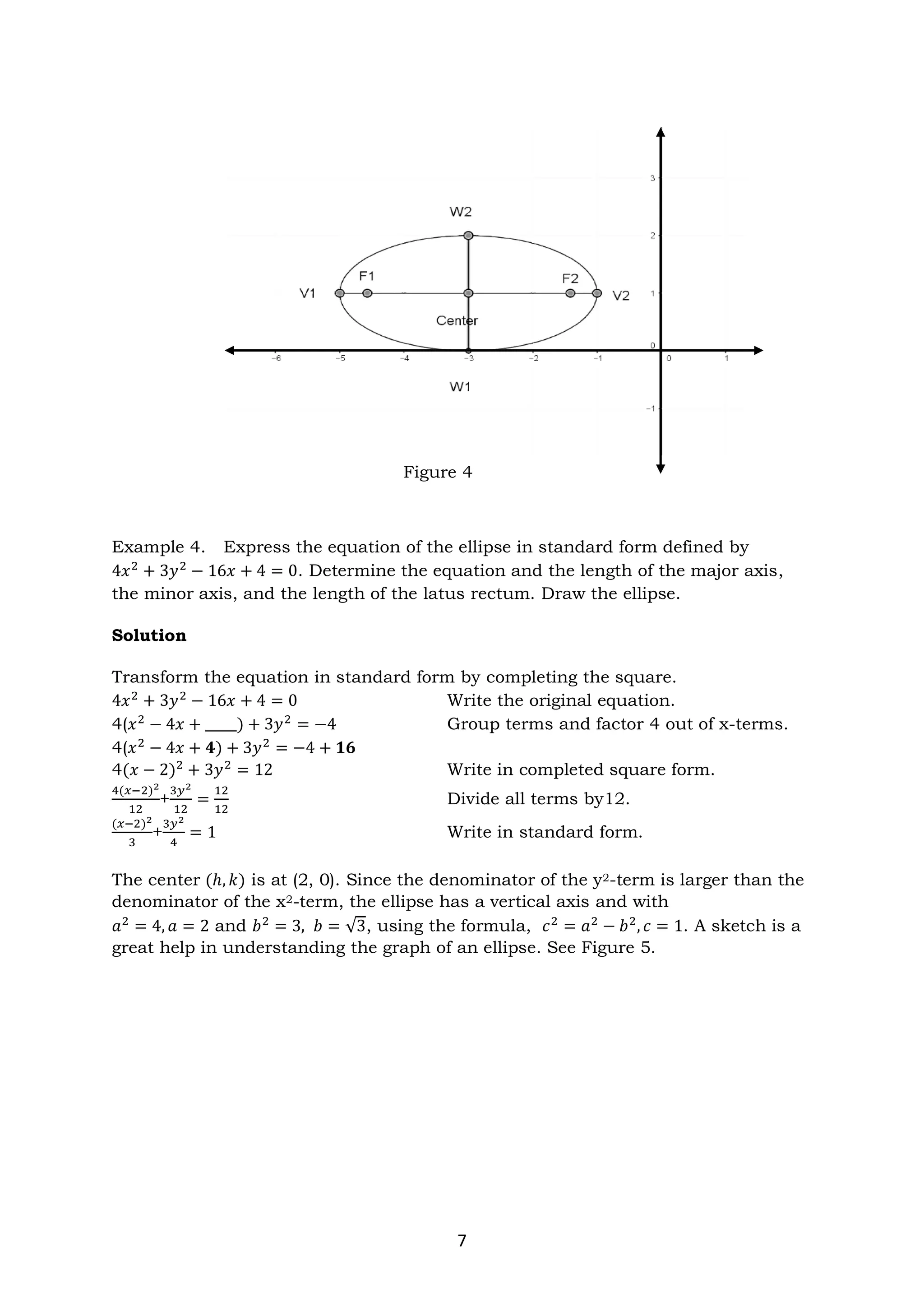
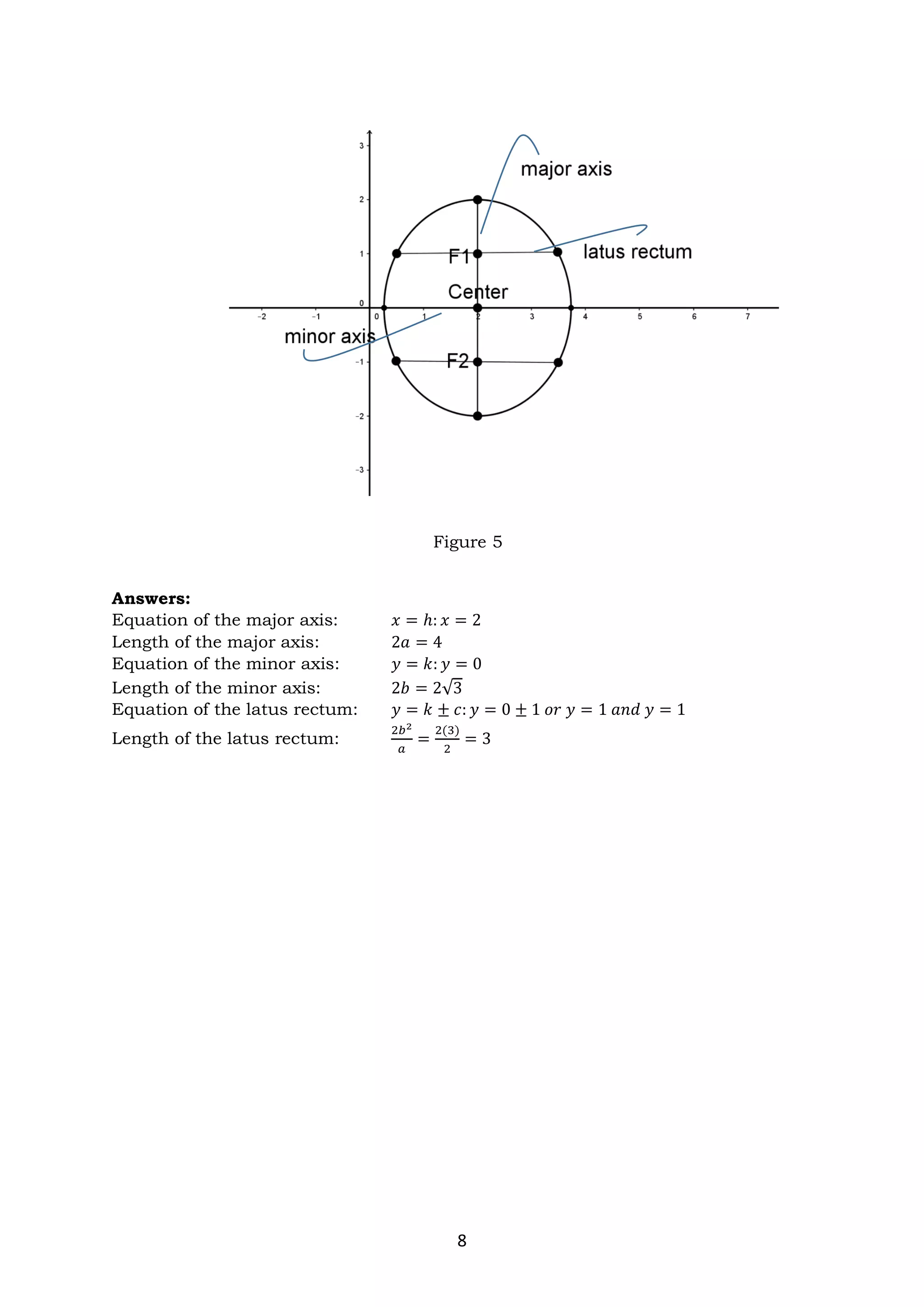
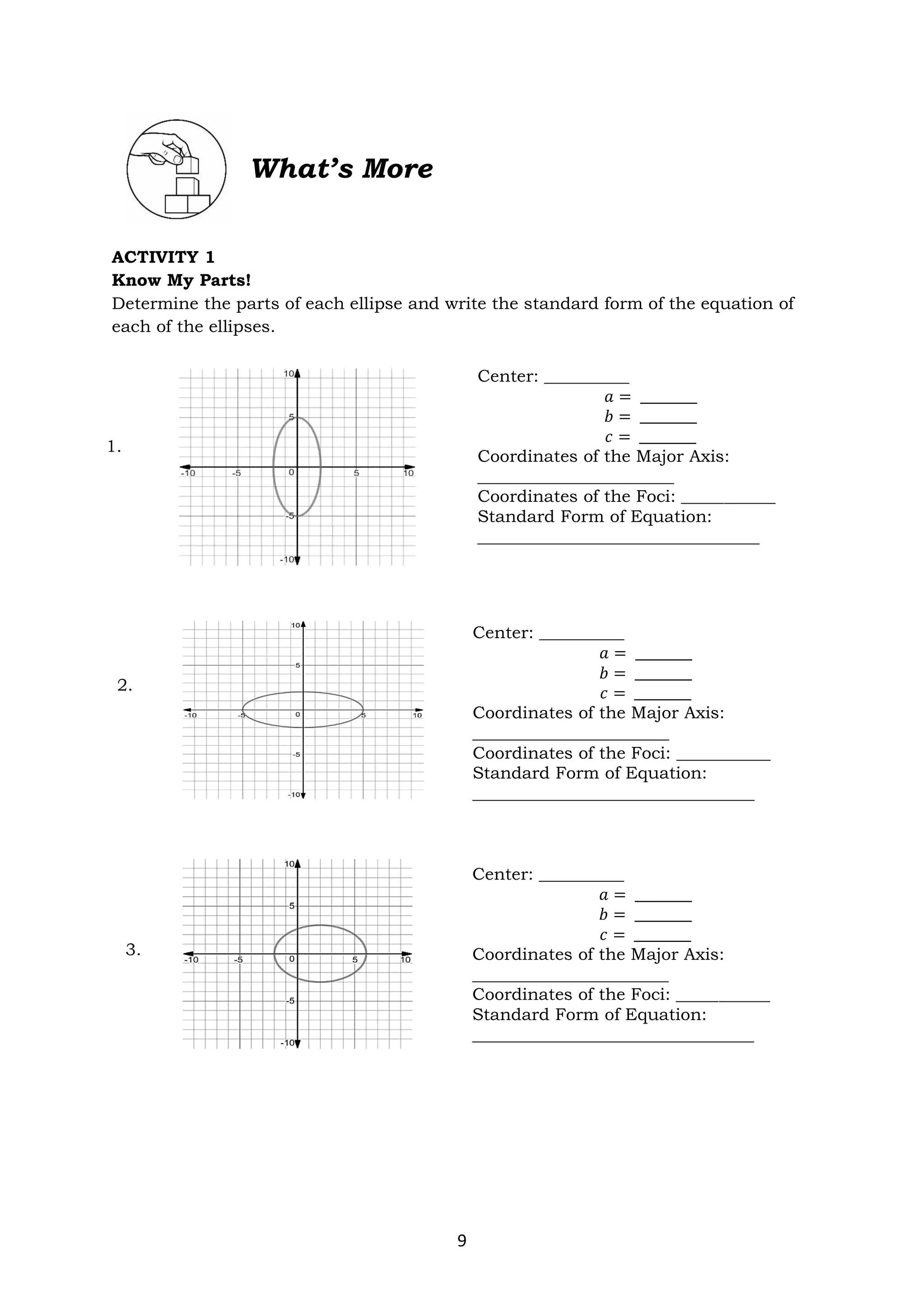
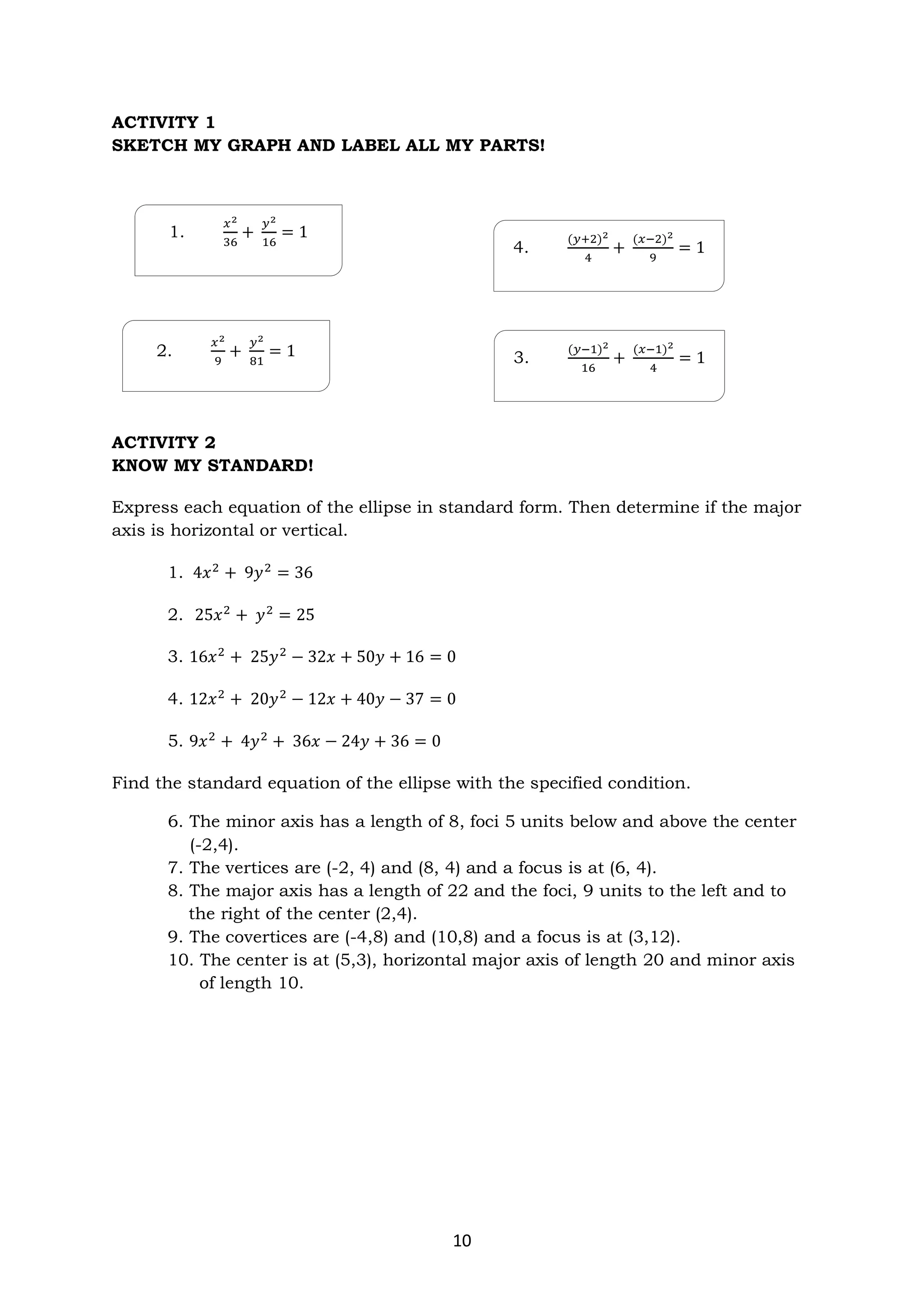
The document discusses ellipses and their key properties. It defines an ellipse as the set of points where the sum of the distances to two fixed foci is constant. Examples are given showing how to identify the center, vertices, covertices, and foci of ellipses given their equations. It also explains how to write the standard form of the equation of an ellipse and determines whether it has a horizontal or vertical major axis. Activities are provided for students to practice identifying parts of ellipses and writing their standard forms from equations.