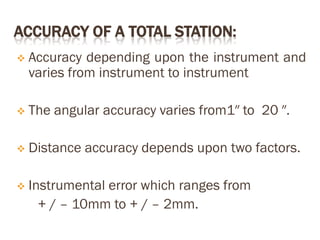
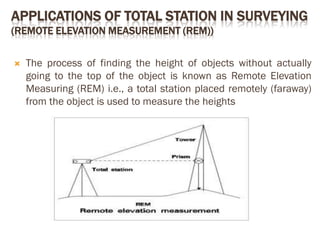
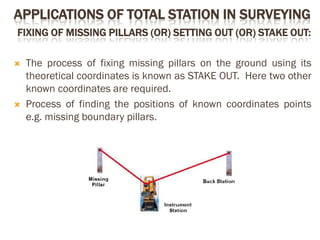
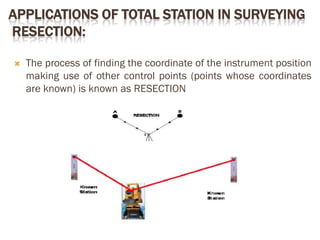
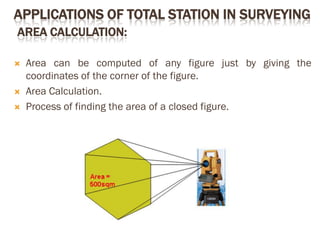
A total station is an electronic/optical instrument used in modern surveying that combines an electromagnetic distance measuring instrument, electronic theodolite, and microprocessor to measure horizontal and vertical angles as well as sloping distances. It has a memory card to store data and battery that provides power for 3 to 8 hours. Total stations can perform functions like averaging measurements, correcting distances, calculating point elevations and coordinates, and have angular accuracy ranging from 1 to 20 seconds and distance accuracy of +/- 10mm to 2mm. They are used for applications like remote elevation measurement, fixing missing pillars, resection, area calculation, and more.