The document summarizes key concepts relating to the US Constitution:
1) It outlines the creation of the US Constitution in 1787 with the separation of powers into three branches of government.
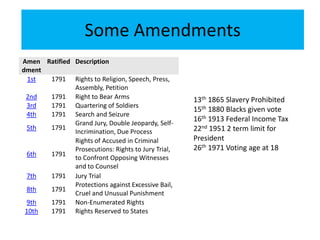
2) It discusses the amendment process and some of the important amendments, especially the Bill of Rights added in 1791 which protect civil liberties.
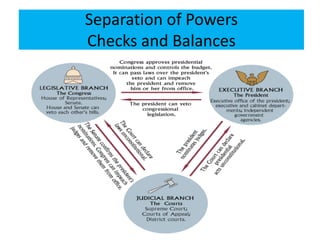
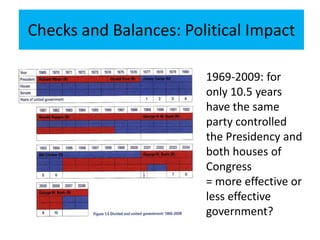
3) It explains the concepts of separation of powers and checks and balances between the different branches of government.
4) It describes federalism as the division of power between the national and state governments, and how this relationship has changed over time with the national government taking on a larger role.