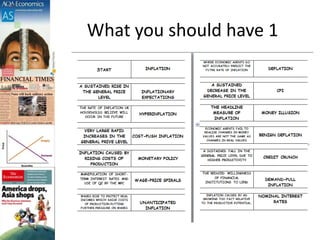
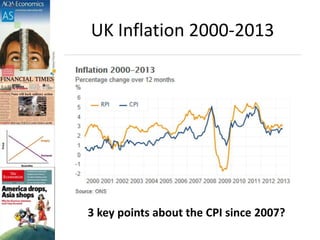
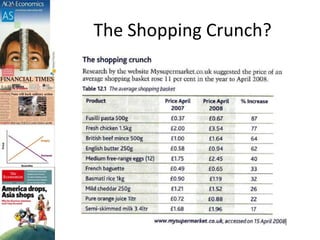
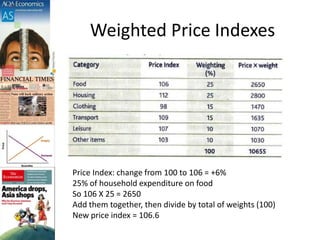
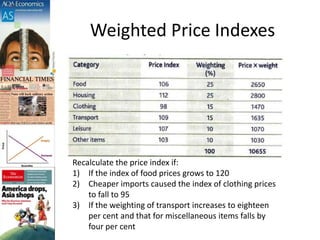
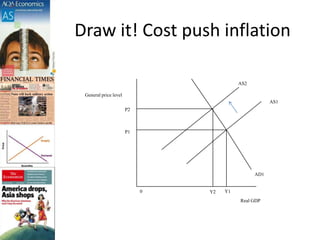
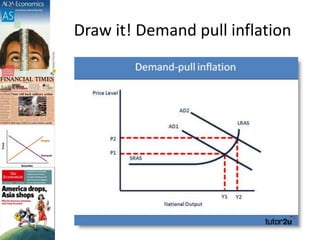
This document discusses inflation and consumer price indexes. It begins by defining inflation as a sustained increase in price levels, which is measured in the UK using the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The CPI is a weighted price index that tracks the prices of goods in a typical household's shopping basket. It has some limitations, as it only measures average inflation and does not account for differences between population groups or include things like house prices. The document then examines causes of inflation, distinguishing between cost-push inflation, which results from rising production costs, and demand-pull inflation, which occurs when aggregate demand increases faster than the economy's productive capacity. Examples of each type of inflation are provided and illustrated with diagrams. Objectives and homework related