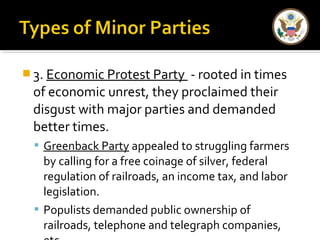
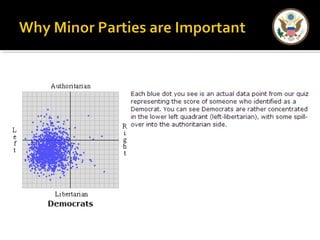
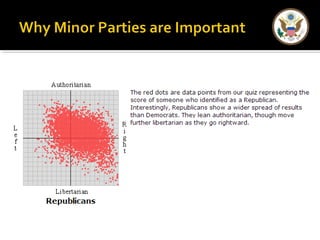
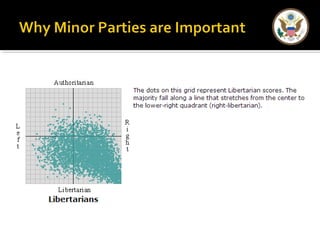
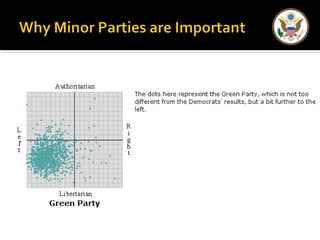
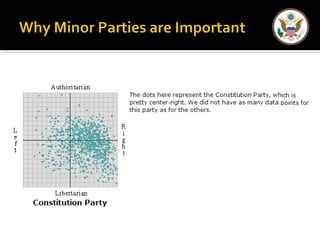
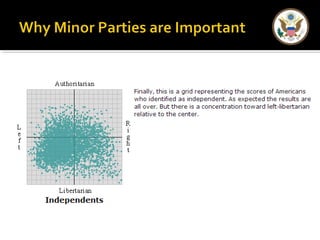
The document provides an overview of political parties in the United States. It discusses how political parties are decentralized organizations without clear central leadership. It also describes the three main components of political parties: the party organization, the party in the electorate, and the party in government. Additionally, it outlines different types of minor parties such as ideological parties, single-issue parties, and economic protest parties. The document also discusses how political parties are organized at the national, state, and local levels.