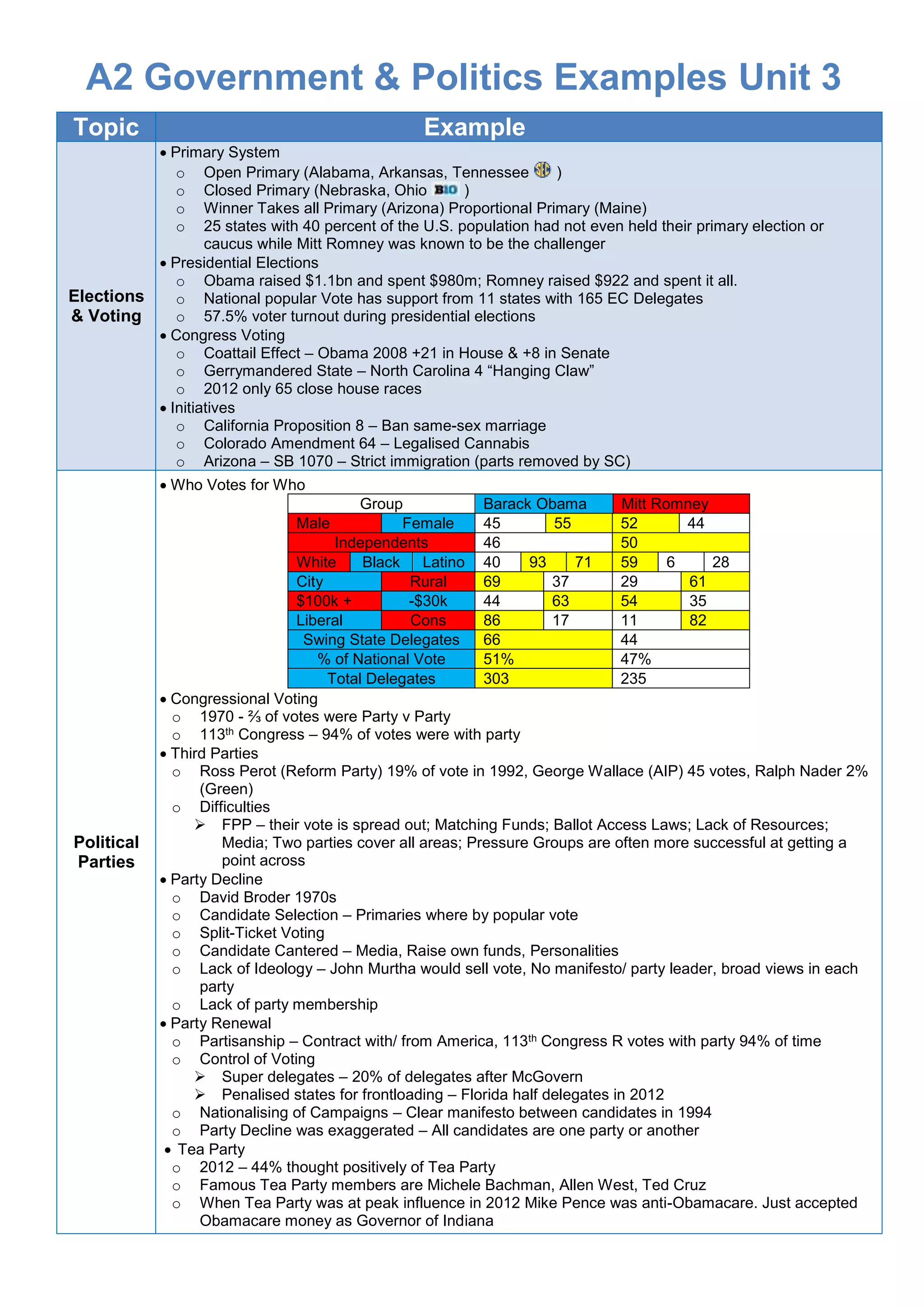
This document provides information on various topics related to government and politics in the United States, including elections and voting processes, political parties, pressure groups, and racial and ethnic politics. It describes primary election systems used by different states, campaign fundraising and voter turnout in presidential elections, and factors that influence congressional voting. It also discusses the decline and attempted renewal of political parties, the roles of prominent pressure groups, Supreme Court rulings impacting racial issues, and debates around affirmative action.