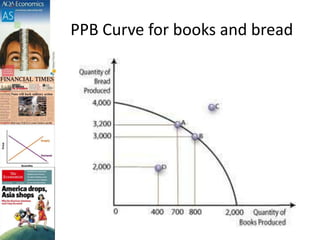
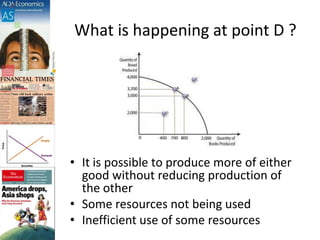
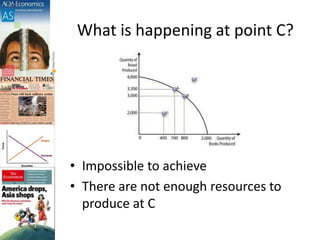
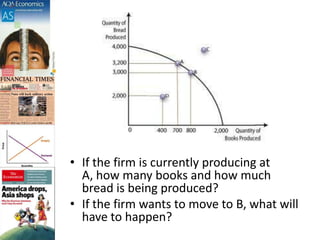
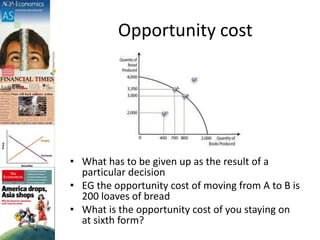
The document discusses production possibility boundaries (PPB) and key economic concepts related to a firm's production of two goods. It explains that a PPB curve on a graph shows the maximum output combinations of two goods a firm can produce with limited resources. Points on the curve represent productive and allocative efficiency, while inside the curve represents underutilization of resources and outside is unattainable. A shift of the curve can occur through acquiring new resources, technology improvements, or greater productivity, benefiting society through increased output.