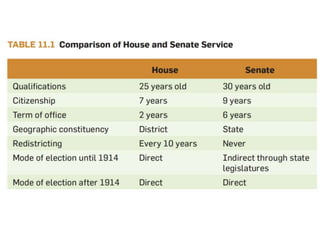
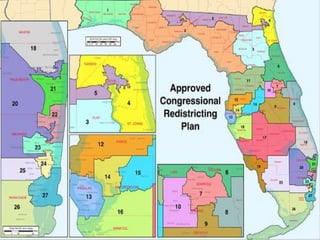
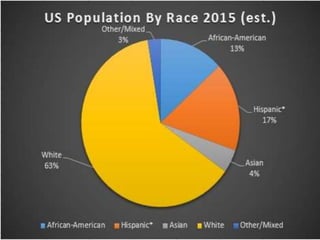
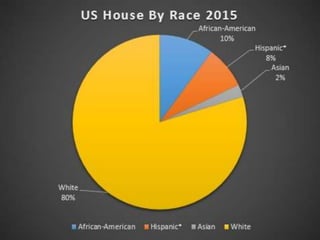
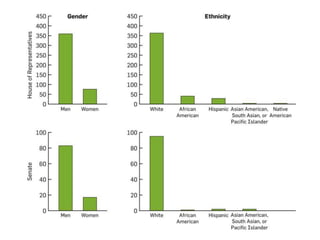
This document discusses the structure and functions of the United States Congress. It outlines that Congress is divided into two chambers, the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House has larger representation based on population, while the Senate provides equal representation for each state. Congress passes laws, declares war, regulates commerce, holds impeachment proceedings, oversees the executive branch, and approves treaties and appointments. Political parties help organize Congress and competing policy positions. Leadership roles include the Speaker of the House, Majority Leader, and committee chairs. The legislative process involves bills being introduced, reviewed in committees, debated on the floor, and sent to the president to be signed into law or vetoed.