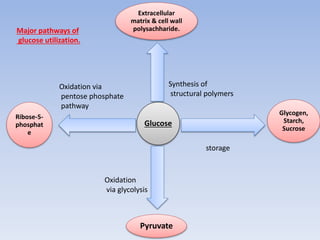
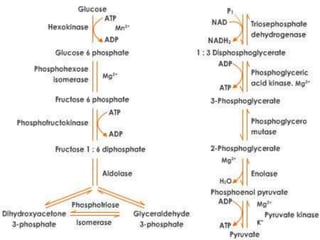
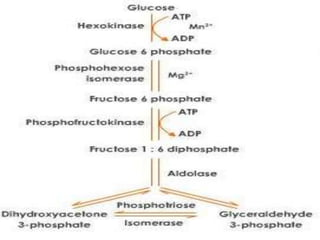
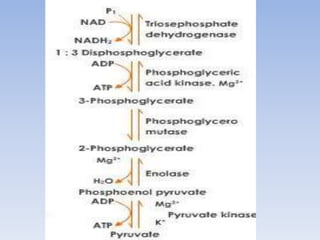
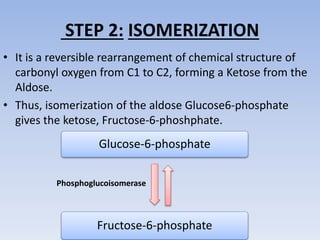
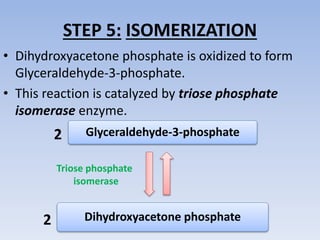
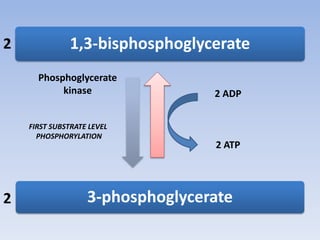
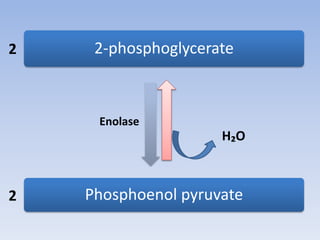
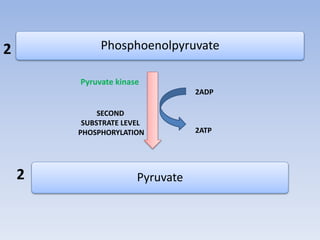
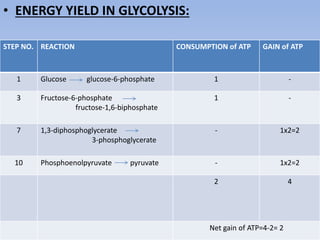
Glycolysis is a 10 step pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH. It occurs in two phases: the preparatory phase requires 2 ATP but produces no ATP, while the payoff phase produces a net of 2 ATP per glucose through substrate-level phosphorylation. Glycolysis is a central and ubiquitous pathway that breaks down glucose as an energy source in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.