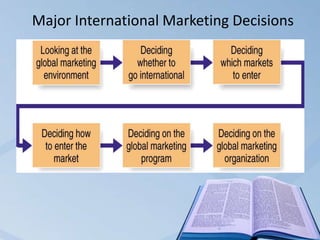
Global marketing involves coordinating marketing activities across countries to create exchanges that satisfy individual, organizational, and societal goals. It evolves from developing a core business strategy, internationalizing that strategy, and then globalizing the strategy. When internationalizing, companies look to increase their customer base, offset risks and costs, and take advantage of opportunities abroad. However, internationalization also presents disadvantages like cultural barriers, regulations risks. Success in global marketing requires balancing local and global concerns through localized implementation with global coordination.