This document discusses various types of risks including:
- Market risk, strategic risk, sales risk, management risk, and budget risk as types of business risks.
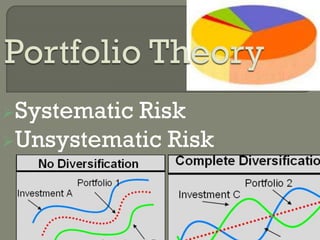
- Systematic risk and unsystematic risk.
- Inflation risk, exchange rate risk, interest rate risk, liquidity risk, maturity risk, credit risk, and political risk.
It provides definitions and explanations of these risks. The document also outlines a process for risk management including identifying risks, analyzing them, ranking them, and developing contingency plans for high probability/high impact risks.