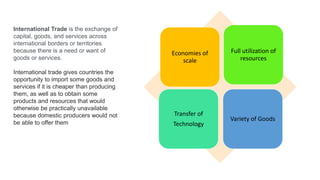
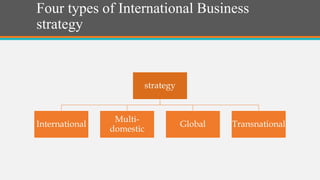
The document discusses international trade and its benefits, including lower costs, access to unavailable goods, economies of scale, and variety. It also discusses India's exports of petroleum, precious stones, pharmaceuticals, and defense goods. International business strategies include international, multi-domestic, global, and transnational approaches. A global information system can collect demographic and consumer data on a global scale to assist companies in developing products for international markets.