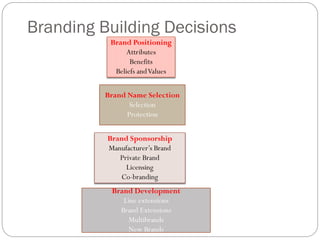
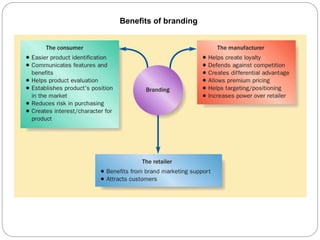
Branding is important for distinguishing products and establishing status. A brand represents the value delivered to customers and builds loyalty. Strong brands are integrated within organizations and drive shareholder value. Key branding elements include the name, position, promise, personality, tone, story and associations. Branding strategies include product, line, range and umbrella branding. Brand management involves marketing programs to build and maintain brand equity through product, price, distribution and communications. New challenges for brands include consumer simplification needs, increased competition and complex portfolios.