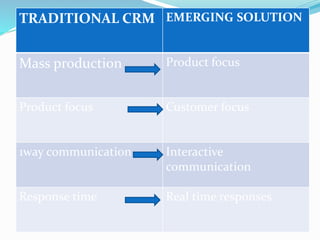
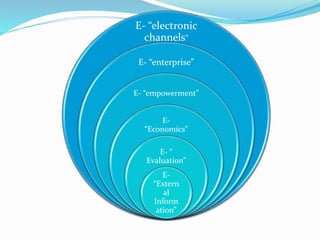
CRM refers to strategies and technologies used by companies to manage interactions with current and potential customers. e-CRM involves applying CRM strategies using electronic channels like websites to personalize the customer experience. Key aspects of e-CRM include tracking customer data online through tools like cookies and web bugs to analyze behavior and personalize marketing. Effective e-CRM systems also integrate data from external sources to gain insights and optimize customer retention, acquisition, and spending. Transitioning to e-CRM requires assessing current capabilities, aligning business strategies, and implementing technical architectures like data mining and campaign management software.