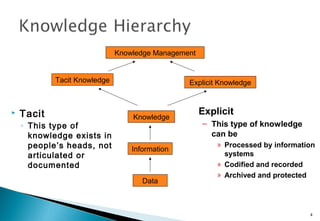
Knowledge management is defined as the explicit and systematic management of vital knowledge and its associated processes of creation, organization, diffusion, use and exploitation. It includes systematically managing and leveraging the stores of knowledge in an organization. Knowledge can be tacit, existing in people's heads, or explicit, able to be processed by information systems and codified. Knowledge assets have become more important than financial assets for companies to gain competitive advantage. Key aspects of knowledge management significance include customer, product, people and process knowledge. Implementation requires getting employee buy-in and making knowledge management a fundamental part of business operations focused on sharing knowledge.