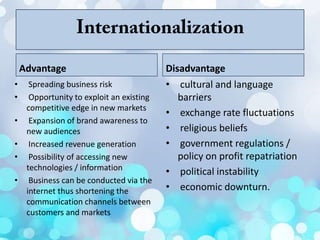
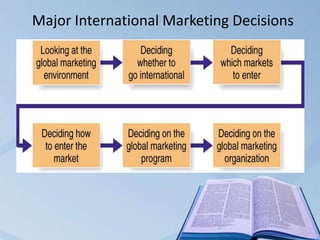
Global marketing involves coordinating marketing activities across different country markets to create exchanges that satisfy individual, organizational, and societal goals. As companies internationalize and globalize their strategies, they must make major decisions about which countries to enter and how using various options like exporting, licensing, franchising, strategic alliances, global or multi-country strategies. When entering new international markets, companies consider factors like political/regulatory environment, financial/economic environment, socio-cultural issues, local competition, and infrastructure. Channel management is developing and aligning customer interfaces like distribution channels across marketing, sales, and services to reach the widest customer base and drive growth and profits.