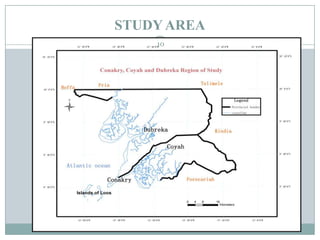
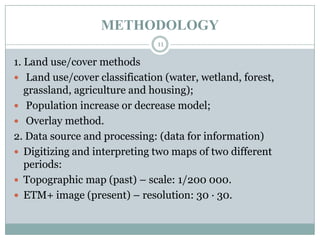
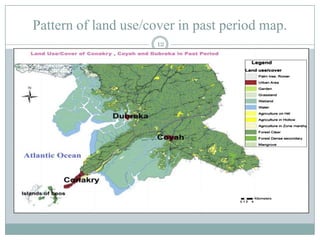
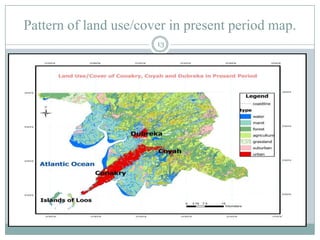
This document discusses the application of GIS in environmental studies. GIS allows for spatial data analysis and overlay of environmental data on digital maps. It can be used to identify hazards, risks, and areas requiring protection. GIS supports environmental assessment, monitoring, and mitigation activities. Field studies can utilize GIS with GPS to accurately map environmental damage. As a case study, the document examines land use/cover changes over time in three regions of Guinea, Africa using GIS analysis of maps and satellite images from different periods. It finds degradation and disturbances, and concludes GIS can help detect changes and potentially propose solutions.