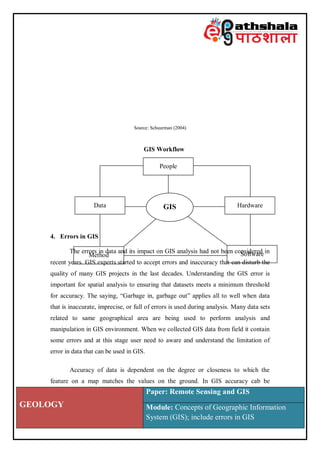
Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, analyzing and managing data and associated attributes which are spatially referenced to the Earth. GIS allows users to visually see relationships, patterns and trends hidden within geographic datasets. It allows analysis and output of geographically referenced data. GIS also refers to spatial information systems and the tools used to gather, store, retrieve, analyze and display geographic or spatial data.