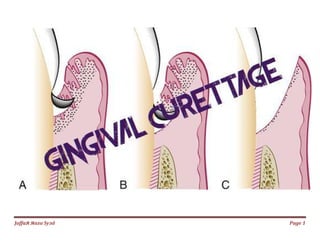
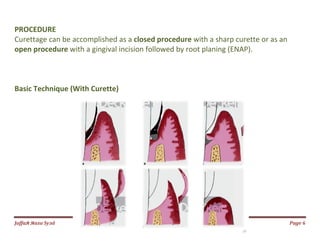
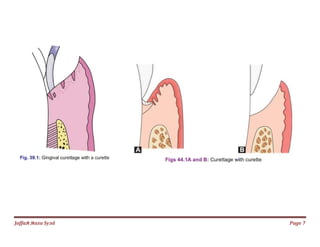
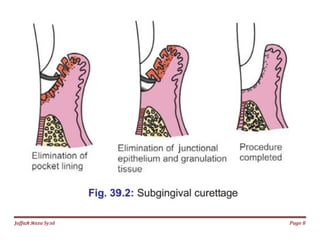
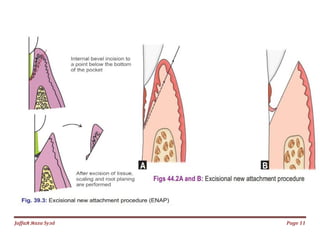
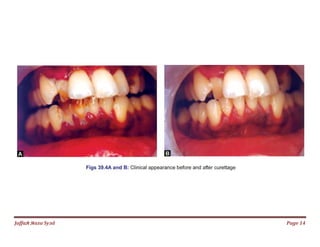
The document discusses gingival curettage, which involves scraping diseased soft tissue from periodontal pockets. It describes different types of curettage including surgical, chemical, ultrasonic, and laser. Indications for curettage include shallow pockets and as maintenance treatment for recurrent inflammation. Contraindications include acute infections and pockets extending beyond the mucogingival junction. The procedure involves scraping the pocket wall with a curette. Excisional new attachment procedure is also discussed, which uses gingival incision followed by root planing. Healing after curettage involves blood clot formation, leukocyte proliferation, and re-epithelialization within 7 days.