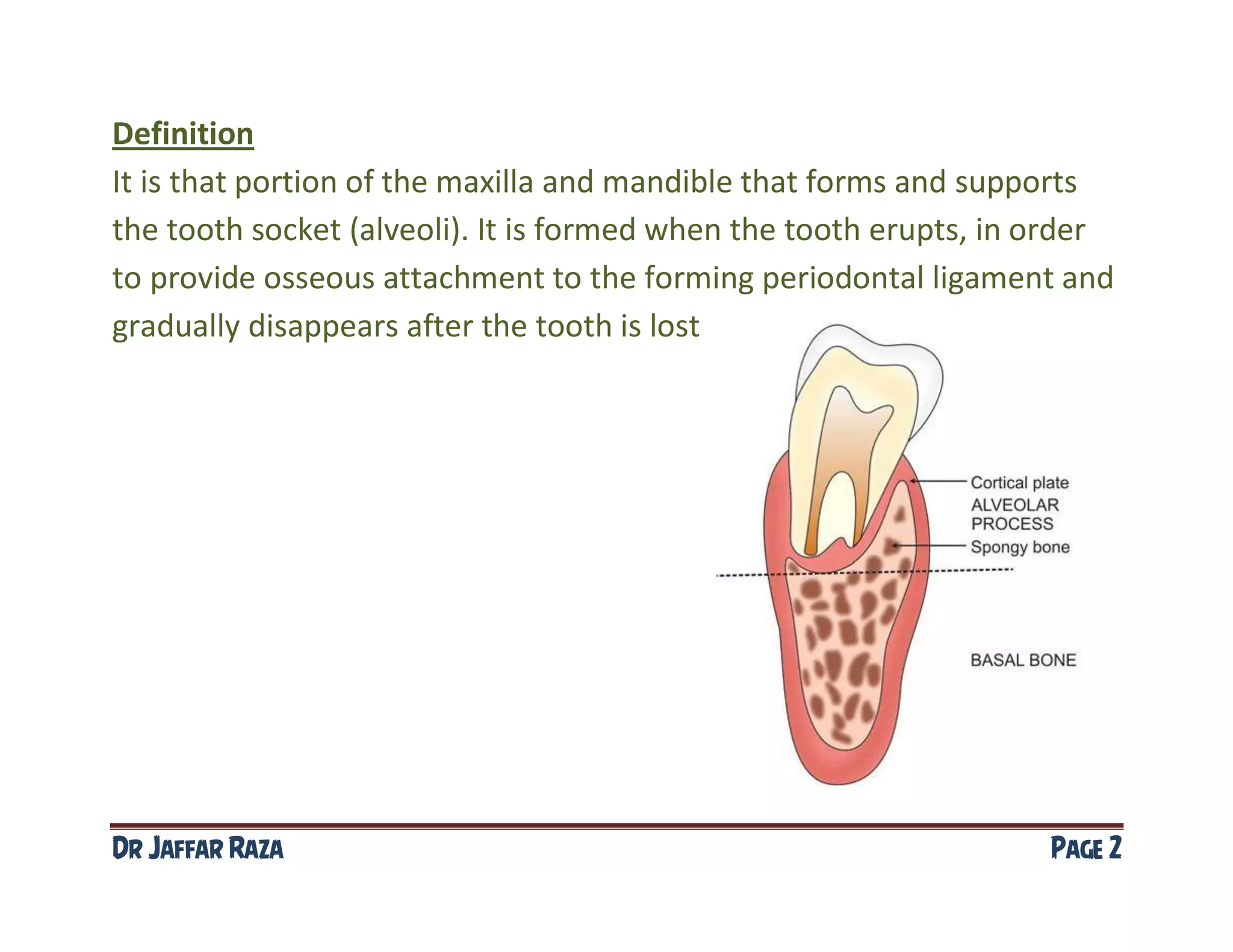
Alveolar bone is the portion of the maxilla and mandible that forms tooth sockets (alveoli) to provide attachment for the periodontal ligament as teeth erupt. It consists of inner and outer cortical plates and cancellous bone lining the socket. The cortical plates and bone lining meet at the alveolar crest, usually 2 mm below the CEJ. Alveolar bone is composed of 67% inorganic hydroxyapatite and 33% organic collagen and non-collagenous proteins that are important for coupling of osteoblasts and osteoclasts during bone remodeling. Bone modeling shapes overall bone size and shape during growth, while bone remodeling continuously replaces old bone with new in a cyclical process throughout life.