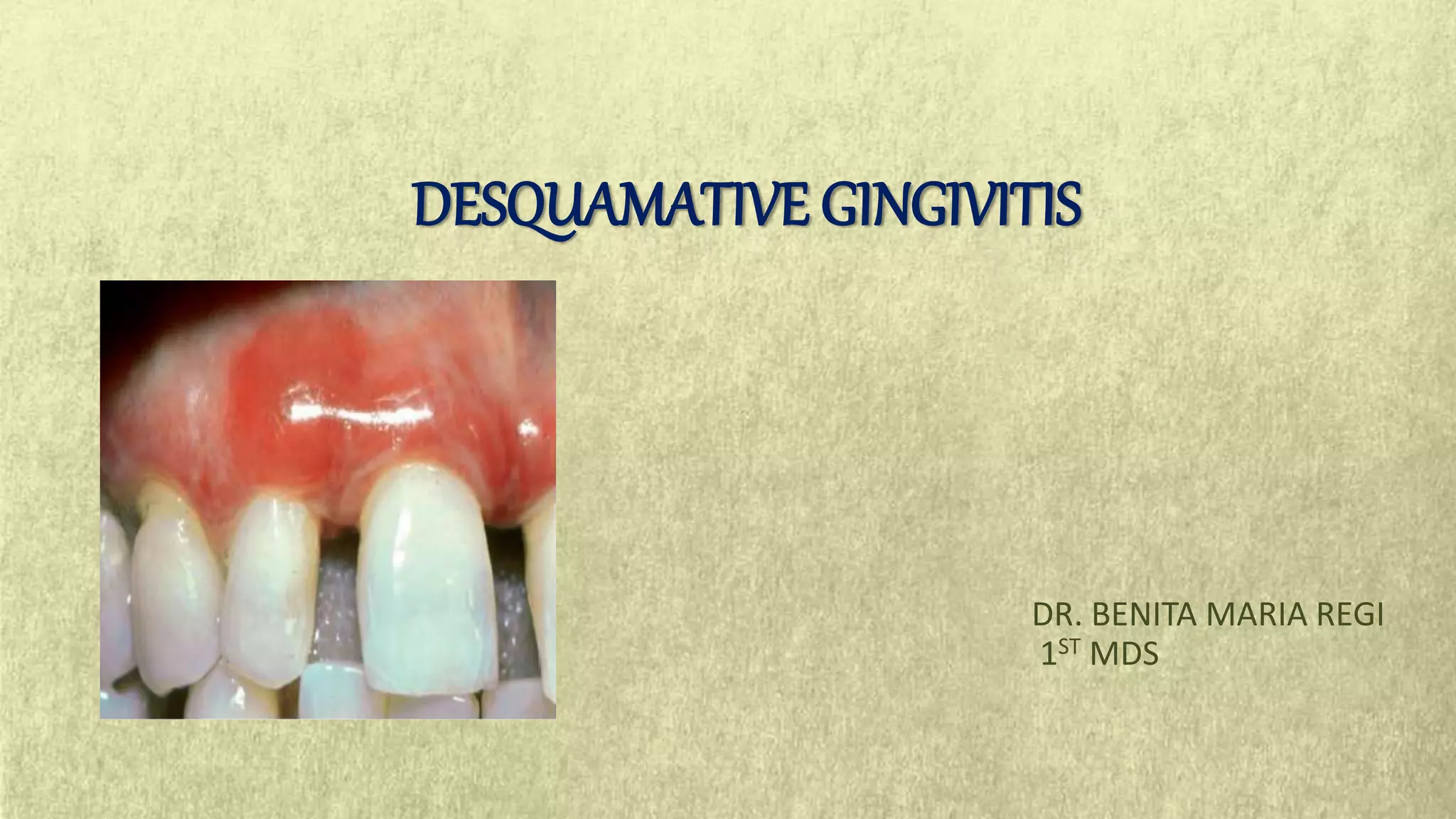
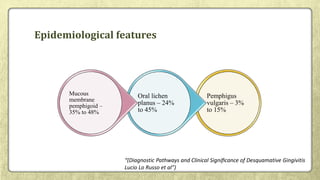
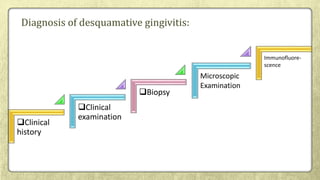
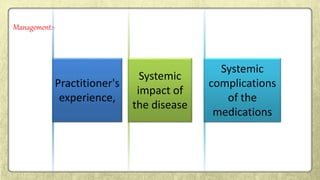
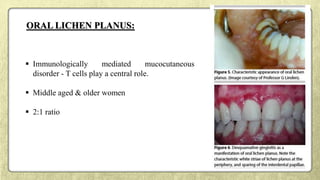
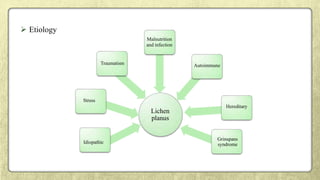
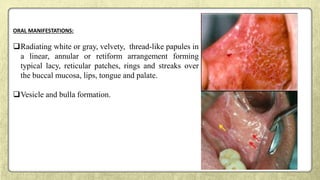
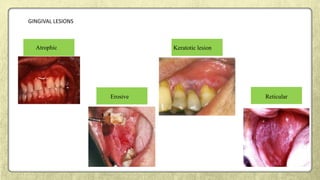
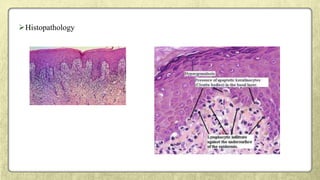
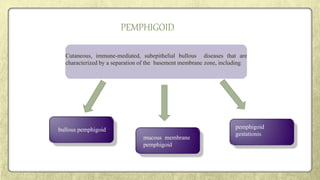
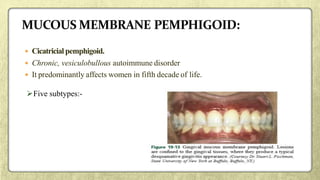
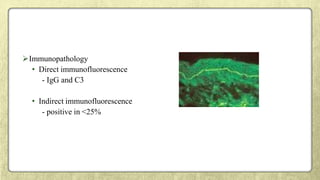
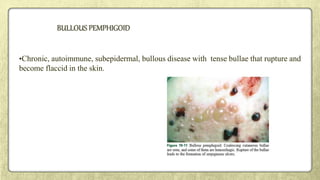
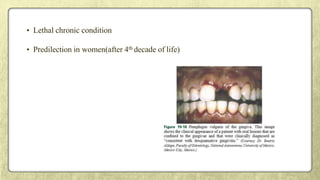
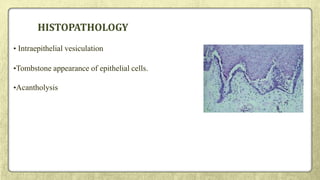
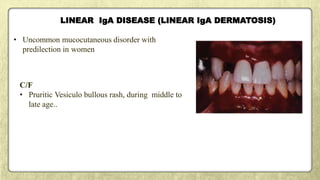
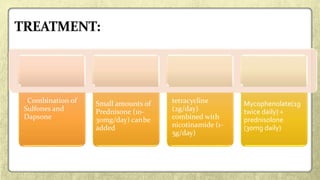
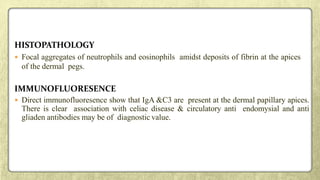
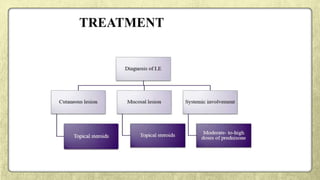
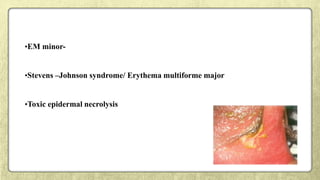
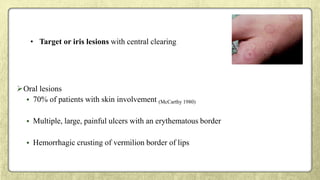
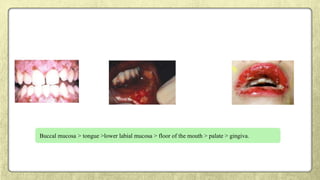
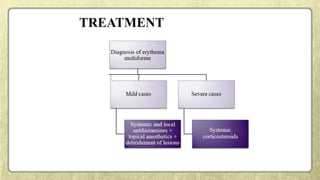
This document provides an overview of desquamative gingivitis (DG), a clinical sign characterized by redness and scaling of the gingiva. It discusses the various diseases that can present as DG, including lichen planus, pemphigus, pemphigoid, linear IgA disease, and lupus erythematosus. It outlines the diagnostic process and significance of DG, noting that the associated disorders can impact oral health and require systemic treatment with corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, increasing risk of complications. Proper diagnosis of the underlying condition is important for effective management of DG lesions and systemic disease.



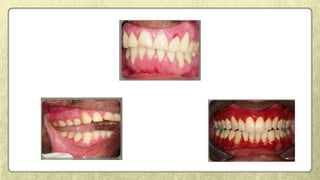





























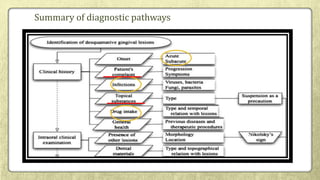
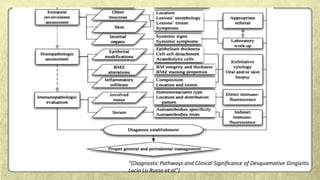




![• On the other hand, a direct effect of DG lesions on periodontitis …..(Kornman, 2008).
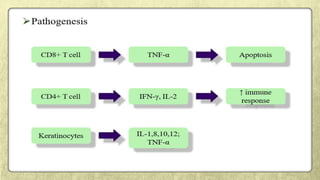
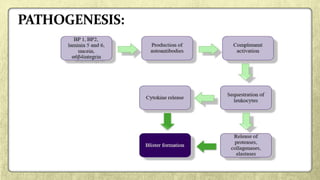
• Immune-inflammatory mechanisms are also critical for the pathogenesis of most of DG-associated
disorders (Lo Russo et al, 2008), which often involves common molecules⁄cytokine networks [e.g. TNF-
a for OLP (Sugerman et al, 2002; Sugermann et al, 1996; Khan et al, 2003)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sem5desquamativegingivitis-180129165858/85/desquamative-gingivitis-74-320.jpg)