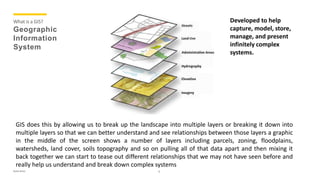
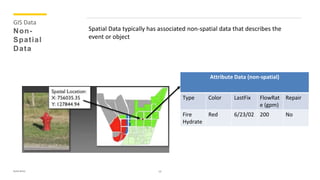
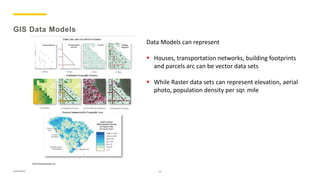
The document presents an overview of geomatics, defining it as a multidisciplinary approach to managing spatially referenced data. It outlines various disciplines within geomatics, such as computer science, geodesy, topography, and geographic information systems (GIS), emphasizing their importance in data collection and analysis. It highlights the critical role of GIS and GPS in applications like petroleum exploration and disaster management by representing and analyzing complex spatial data.