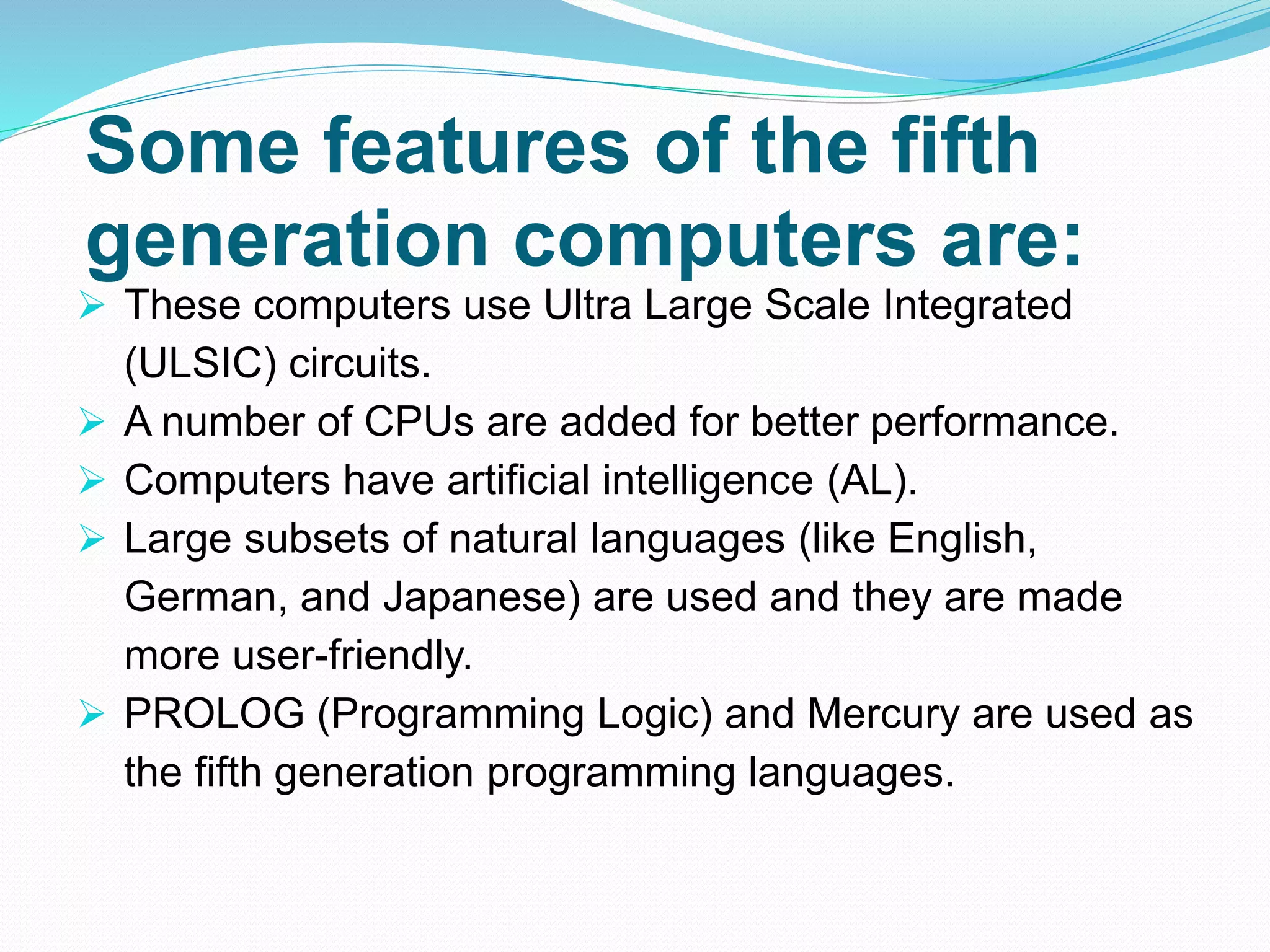
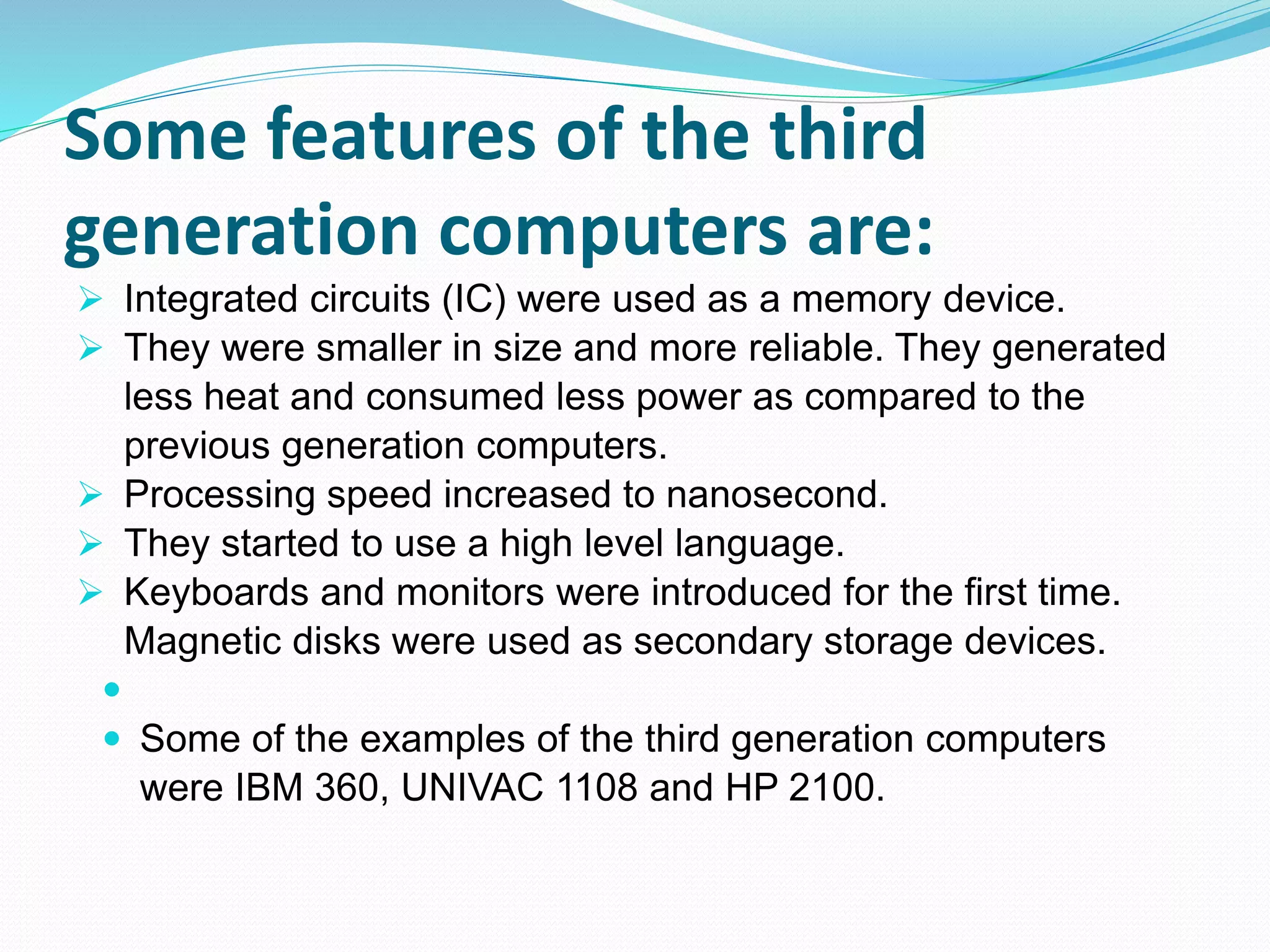
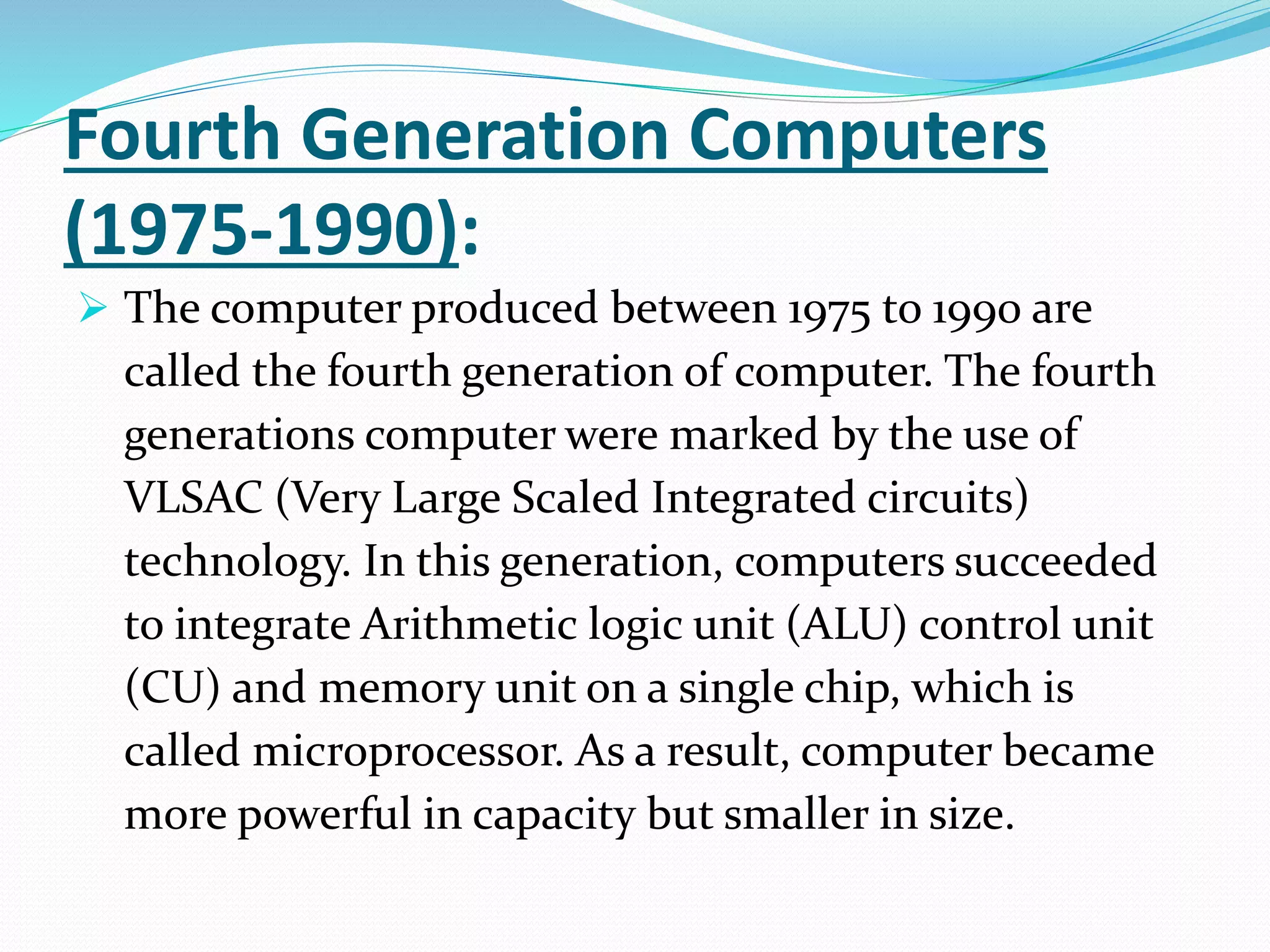
The document summarizes the five generations of computers from the first to fifth generation. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were large, unreliable, and expensive. The second generation used transistors, were smaller and more reliable. The third generation used integrated circuits, were faster and introduced keyboards/monitors. The fourth generation used microprocessors and were powerful yet small. The fifth generation has artificial intelligence capabilities.



![Third Generation computers
(1965-1974)
The computers produced and used between 1965 and
1974 are called the third generation computers .The
third generation computers were marked by the use of
IC [Integrated Circuit] instead of a transistor .They
were smaller in size ,faster and more reliable than the
second generation computers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generationsofcomputer-200925003510/75/Generations-of-computer-7-2048.jpg)

![Fifth Generation Computer
(1991 onwards):
The first microprocessor, Intel 4004 was 4 bits
microprocessor. The major shortcoming in the earlier
generation was lack of thinking power .The fifth
generation computer system project was initiated by
Japan’s Ministry of International Trade and Industry in
1982 .The fifth generation computers have artificial
intelligence [AI] . AI refers to the human behaviors put
in the computer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generationsofcomputer-200925003510/75/Generations-of-computer-11-2048.jpg)